Synthetic Biology Applications: Global Overview
Imagine a group of university students meeting in a small biology laboratory. They are excited and nervous. Their project is all about designing a bacterium that can clean oil spills in the ocean. With a few genes, a simple lab setup, and a big dream, they begin creating what nature never made before. This is no longer science fiction. It is because of Synthetic biology. It is the field where imagination meets DNA.
This was once a classroom dream, and today it’s turning into global innovation. Synthetic biology, more often called “SynBio,” is one of the fastest-growing fields. It shapes the future of medicine, agriculture, the environment, and even space.
In this article, let’s get to know exactly what Synthetic Biology means and why it matters for every student who aspires to be part of the next biotech revolution.
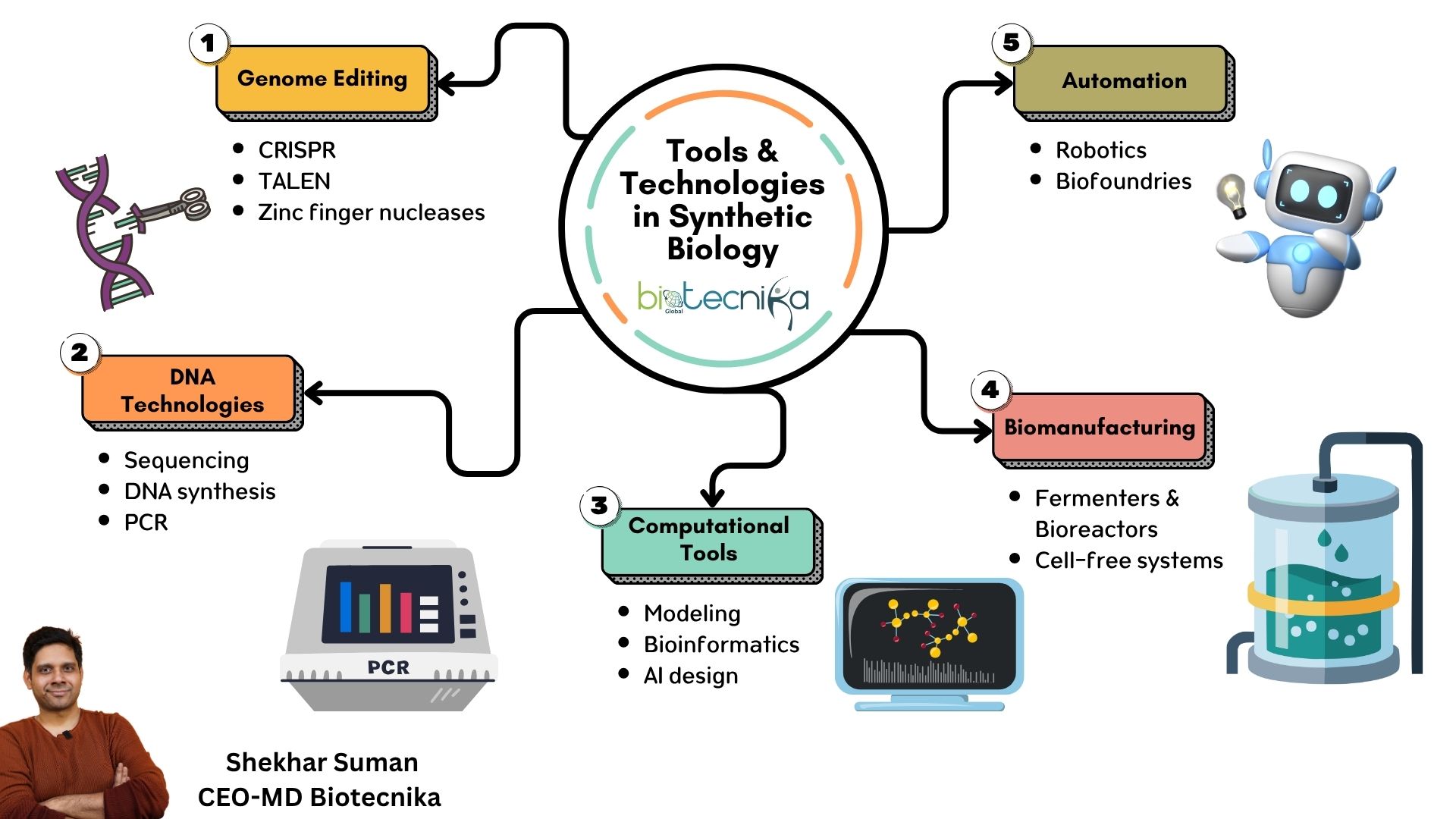
What is meant by Synthetic Biology?
Synthetic biology is the science of designing and creating new biological parts, systems, and organisms. It is similar to engineering, except that instead of working with metals and circuits, genes and cells are what scientists and researchers use as their building blocks. This mostly happens with the help of Recominant DNA Technology. rDNA Technology involves cutting and pasting of genes to create new genetic material containing organism.
I want you to think of it this way: if traditional biology studies how nature works, synthetic biology asks “Can we build something new that nature never made?”
It combines knowledge from genetic engineering, computer science, and chemistry in order to create living systems that solve real-world problems, ranging from the production of sustainable fuels to fighting climate change.
Why it Matters for Students?
To students, synthetic biology goes beyond a mere subject. It leads their career and opens doors toward research, startups, and industries reshaping the global economies. And the best part? Many groundbreaking SynBio projects started from students participating in international competitions-like iGEM, or International Genetically Engineered Machine-where teams design new, unique biological solutions for global problems.
- Healthcare Innovations:
Synthetic Biology is revolutionizing a lot in medicine. It helps in the ways of treatment and drug production. Instead of the traditional drug discovery, nowadays scientists design living cells acting as mini-factories to produce life-saving components.
- Synthetic vaccines: Through the work of Synthetic Biology, vaccines have been produced to help during the COVID-19 pandemic. Using Synthetic mRNA, companies like Moderna and BioNTech have taught our bodies to effectively fight the virus.
- Engineered probiotics are bacteria engineered by scientists to live in our intestines and thereby facilitate disease treatment, such as diabetes or Crohn’s disease, by releasing therapeutic molecules.
- Personalized medicine: Synthetic Biology tools can make therapies that correspond with an individual’s genetic profile, offering personalized treatment instead of one-size-fits-all drugs.
- Food and Agriculture:
The world’s population is growing fast, but crop field is not! Synthetic Biology offers solutions that make food production smarter and more sustainable.
- Synthetic crops: Scientists make modifications in the genes to develop plants that require less water, are resistant to pests naturally, and give higher yields.
- Clean Meat: Animal cells are grown into meat in a laboratory to make clean meat. It helps reduce greenhouse gas emissions and animal suffering. Startups like Upside Foods and Mosa Meat spearhead this food revolution.
- Bio-fertilizers: Genetically modified microorganisms improve nutrient uptake from the soil by plants, reducing the amount of hazardous chemical fertilizers.
These innovations are targeted at creating a climate-resilient agriculture system, as no one should go hungry in the future.
- Environmental Protection:
Synthetic biology is turning biology into a tool for planetary repair.
- Plastic-eating bacteria: Scientists have developed microbes capable of degrading plastics. This helps to reduce ocean pollution.
- Carbon Capture: Carbon-Capturing Bacteria are created to absorb Carbon dioxide from the atmosphere to combat global warming. Bio-remediation: Synthetic microorganisms are able to clean up oil spills, industrial waste, and toxic metals from contaminated areas.
These applications bring hope for a cleaner, greener planet.
- Energy and Industry:
Energy production is one of the greatest challenges in daily lives. Synthetic Biology is driving a bio-based economy. Instead of fossil fuels, it is creating fuels and materials from renewable sources.
- Biofuels: Engineered yeast and bacteria make ethanol or diesel from sugar and waste.
- Bio-manufacturing: Scientists engineer cells to create chemicals, fabrics, and even perfumes in an eco-friendly manner. Example: Synthetic Spider Silk is stronger than steel. But it is biodegradable and used to produce surgical threads.
This approach reduces pollution and the dependence on non-renewable energy.
- Space Exploration:
Synthetic biology is also helping humans get ready for space missions. It is not possible to carry all the resources for the astronauts who go to Mars or the Moon. Scientists are creating microbes that can produce oxygen, food, and medicines in space. This is making distant planets into livable habitats. NASA’s SynBio programs are using genetically modified microorganisms for life support systems.
- Education and Careers:
Synthetic Biology is not just about learning science for the students. It is about creating opportunities. Various universities around the world now offer specialized programs in SynBio, putting together biology, data science, and engineering.
Top global institutions leading in synthetic biology research include:
| University | Country | Focus Area |
| MIT (Massachusetts Institute of Technology) | USA | Bioengineering, SynBio startups |
| Imperial College London | UK | Biodesign, metabolic engineering |
| ETH Zurich | Switzerland | Industrial biotechnology |
| National University of Singapore | Singapore | Synthetic gene circuits |
| IISc Bangalore | India | Genetic design and biosystems |
- Safety Concerns and Ethics
Discoveries create more responsibilities. Synthetic biology raises important ethical questions: Should humans design life? What if the genetically engineered organisms were to escape into nature?
There are strict biosafety guidelines provided by various governments and global organizations with respect to safety measures. Many research groups follow a “safe by design” approach so that each synthetic microbe will be controllable or inactivated if needed. In the process of learning SynBio, students are also encouraged to study bioethics, making innovation safe, ethical, and beneficial through SynBio Certification Courses.
- Global Impacts and Future
Synthetic Biology is becoming an important aspect of global innovation right from saving lives to saving the planet. With thousands of startups raising across healthcare, environment and energy sectors, the global SynBio market is projected to cross 60 billion dollars by 2030. It is a future where your biology project could turn into the next global solution. As one iGEM student once said, “Synthetic biology is not about changing life. It is about having enough understanding to create something greater.
Synthetic Biology for a Sustainable Future
Synthetic Biology is creating a sustainable, healthier, and greener world, with the UN Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs).
SDG 2:
This demonstrates Zero Hunger by the production of Genetically Modified Crops. The goal is to end hunger and ensure food security for all.
Role:
- Genetically modified plants are created by Scientists that grow faster, use less water, and resist pests naturally.
- Biofertilizers are being produced by Synthetic microbes that improve soil health.
- Engineered yeast and bacteria help create plant-based proteins, reducing the pressure on traditional farming.
- Example: Golden Rice enriched with Vitamin A to fight malnutrition in developing countries.
SDG 3:
This demonstrates Good Health and Well-Being by the production of New Drugs & Diagnostics. The main goal is to ensure healthy lives and promote well-being for all.
Role:
- New Drugs are produced in a faster rate and cheaper way using genetically modified microbes instead of animal testing or rare plants.
- COVID-19 Vaccine are developed using mRNA Technology are created by synthetic biology.
- Diseases can be detected early using Synthetic biosensors. For example, researchers use bacteria that can glow while detecting toxins or infections.
- Example: Genetic disorders like cystic fibrosis and sickle cell anemia may be cured by New gene therapy.
SDG 7:
This demonstrates Energy that is affordable and clean through the production of Biofuel. The goal is to make sure that modern energy is accessible, affordable, reliable, and sustainable for everyone.
Role:
- Ethanol and biodiesel are produced by genetically modified algae and microbes from waste materials.
- Synthetic enzymes improve energy efficiency in chemical processes.
- Example: Genetically modified cyanobacteria that use sunlight to directly produce hydrogen fuel.
SDG 13:
This demonstrates that Climate actions can be predicted by producing genetically modified organisms. The main goal is to predict and fight climate change and its impacts.
Role:
- Bioplastics and Biofuels are produced by Carbon-eating microbes. They absorb CO₂ and convert it into useful materials.
- Synthetic trees and bioengineered bacteria can mimic photosynthesis to reduce greenhouse gases.
- Biodegradable plastics are created by Synthetic biology. This helps in reducing plastic pollution.
- Example: The genetically modified microorganisms of LanzaTech to convert industrial emissions into sustainable jet fuel.
The Future is You
Synthetic biology is much more than science. It is a full-on expression of creativity, curiosity, and care. Whether you’re a high school student into genes or a researcher building new bio-tools, your ideas could help solve unimaginable challenges in the world. We are in a new era of biology; students today are not just learners but creators of the future.