What Are Stem Cells? Types, Functions & Their Role in Regenerative Medicine
Imagine for a moment that you are renovating a historic house. You have a pile of specialized materials, such as hardwood for the floors, tiles for the bathroom, and shingles for the roof. But what if you had a magical material, Clay that is shapeshifting and which could transform into wood, glass, copper, or brick depending on where you placed it? That is the best way to understand Stem Cells. In the complex architecture of the human body, stem cells are the magical raw materials. They are the biological blank slates from which all the other cells with special functions arise. Under the right conditions, stem cells divide to form more cells called daughter cells.
These Stem cells have been the “Holy Grail of modern medicine” for decades. But what exactly are they? What are its different types? And are they really important for curing diseases? Let’s get to know about the Stem cells and the fascinating reality of regenerative medicine in this article.
What are Stem Cells?
To understand a stem cell, you first have to understand what a cell is. Many of the cells in the body are specialized. A red blood cell carries oxygen, and it cannot suddenly decide to become a nerve cell and send signals to your brain. A muscle cell contracts, and it cannot change into a skin cell to protect you from the sun. They have a career, and they stick to it until they die.
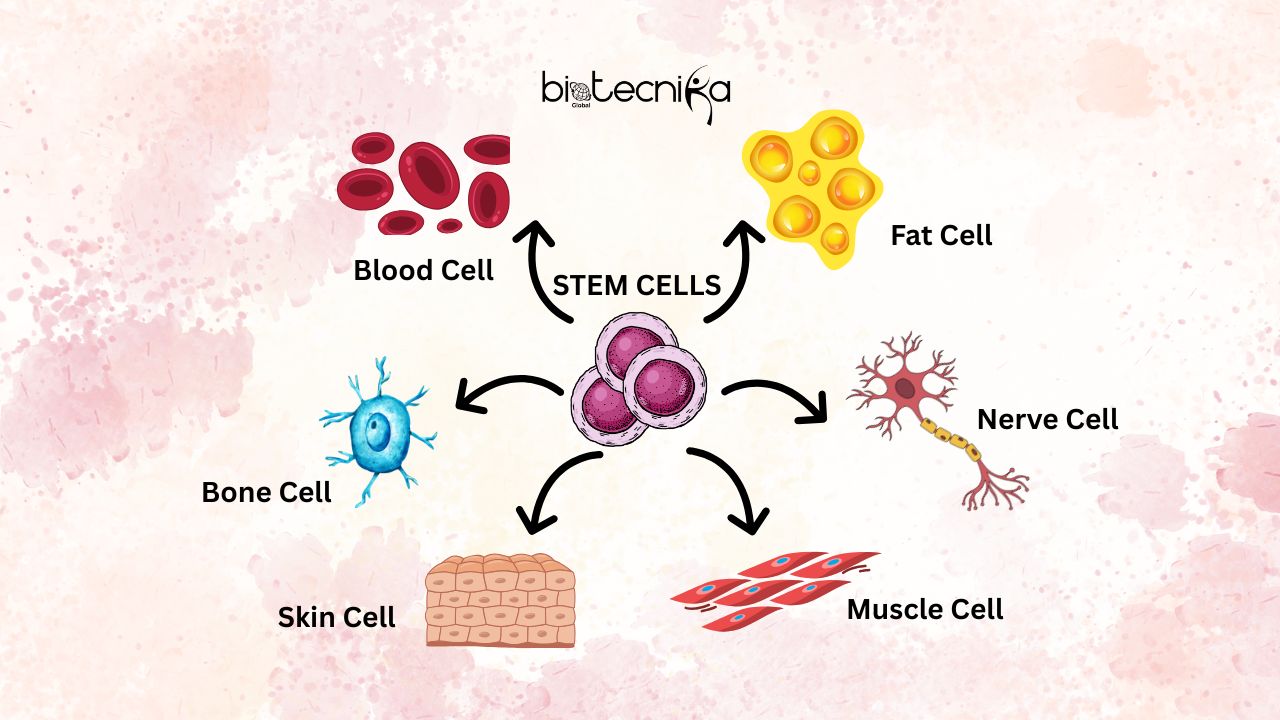
But if you see in the case of Stem cells, they are very different because they are unspecialized. They have not picked a career yet. They possess two unique superpowers that make them different from every other cell type.
- They can make identical copies of themselves again and again and are known as self-renewable. They are like a photocopier that never runs out of paper or ink.
- They can develop into specialized cells such as heart muscle, brain, tissue, and blood cells with specific functions.
Types of Stem Cells
Not all the Stem cells are equally created. Some are with limitless potential, while other are more restricted. Scientists categorize them based on their potency, especially how many different types they can become. The types of Stem cells are given below,
- Totipotent (The “Everything” Cells)
The Totipotent Stem cells are the most powerful cells that exist in the body. They occur only in the very first few divisions after a sperm fertilizes an egg. It can form a whole new human being with the placenta.
- Pluripotent (The “Any-Body-Part” Cells)
As the embryo grows into a blastocyst at 3-5 days, the cells lose the ability to make a placenta. But it can still become any cell in the human body. These are often referred to as Embryonic Stem Cells (ESCs)
- Multipotent (The “Specialists”)
These are also known as Adult Stem Cells. You might have these in your body right now! They are found in specific tissues, such as bone marrow, fat, and skin. However, they are limited. A blood stem cell in your bone marrow can make red blood cells, white blood cells, or platelets, but it cannot make a brain cell. When you cut your skin or break a bone, these cells rush to repair the specific damage.
- Induced Pluripotent (The “Time Travelers”)
This is the game-changer. Scientist Shinya Yamanaka discovered a way to take a regular adult skin cell and reprogram it back into an embryonic-like state in 2006. These are called iPSCs. This method bypasses the ethical issues of using embryos and allows doctors to potentially create stem cells from a patient’s own body. This helps in reducing the risk of graft rejection.
|
Type of Stem Cell |
Career Analogy | What They Can Become | Where They Are Found |
| Totipotent | The Newborn Baby | Anything. They have zero limitations. | Only in the first few days after fertilization. |
| Pluripotent (Embryonic) | The University Student | Almost anything. They haven’t picked a major, but they are part of the system. | Early-stage embryos (Blastocysts). |
| Multipotent (Adult) | The Experienced Professional | Specialized within a field. A lawyer can switch firms, but can’t suddenly become a surgeon. | Bone marrow, fat, skin, brain, gut. |
| Induced Pluripotent (iPSCs) | The Career Pivoter | An experienced professional who goes back to school to start over entirely. |
Created in a lab from adult skin/blood cells. |
How Does Stem Cell Biology Actually Work?
You must be wondering, “If I have stem cells in my body, why don’t I regrow a limb if I lose one?” While salamanders can do that, humans have limits. In our body, the adult stem cells act primarily as a repair system. They hang out in niches. They stay quiet in the corner of the tissues and wait for a signal. When an injury or infection occurs, the body sends out chemical signals.
- Activation: Due to the chemical signals, the stem cells wake up.
- Proliferation: Then they divide rapidly to increase their numbers.
- Migration: Then they move toward the site of the injury.
- Differentiation: They transform into the specific tissue needed for the repair.
However, as we age, the numbers and efficiency of our stem cells decline. This is why a toddler heals a scraped knee in days, whereas adults might take weeks to heal a similar wound.
The Role of Regenerative Medicine Stem Cells
Regenerative medicine is precisely what it sounds like, replacing, engineering, or regenerating human cells, tissues, or organs to restore normal function. This is where stem cells move from biology textbooks to life-saving treatment. The regenerative medicine stem cells are helpful in the treatment of various diseases.
- The Success Story: Bone Marrow Transplants
We often talk about stem cells as future technology, but we have been using them for more than 50 years. A bone marrow transplant is a stem cell therapy. Doctors use chemotherapy to wipe out a Leukemia patient’s cancer-ridden bone marrow. They infuse healthy stem cells from a donor into the recipient. These cells migrate to the bone marrow and rebuild the entire immune and blood systems from scratch.
- The New Frontiers
Beyond blood cancer, researchers are looking at three massive areas:
1. Type 1 Diabetes
In Type 1 Diabetes, the body attacks its own insulin-producing cells in the pancreas. Currently, the researchers are using stem cells to grow new insulin-producing cells in the laboratories. These cells could be implanted into a diabetic patient to produce their own insulin.
2. Heart Disease
When a person gets a heart attack, a part of the heart muscle dies and turns into scar tissue. This scar tissue does not beat, weakening the heart. Researchers are injecting heart muscle cells into damaged heart tissues to remuscularize the wall and restore pumping power.
3. Neurodegenerative Diseases
Diseases like Parkinson’s and Alzheimer’s are neurodegenerative. They are involved in the death of specific neurons. In Parkinson’s, it is the dopamine-producing cells. Clinical trials are going on where the lab-grown dopamine neurons are transplanted into the brains of patients.
The “Miracle Cure
If you Google “Stem cell therapy” today, you will be able to find hundreds of private clinics offering treatments for knee pain, anti-aging, autism, and hair loss. But you must be careful and mindful before you jump into those treatments. While Science is promising, regulation has not kept pace. Many private clinics offer unproven stem cell therapies. They usually get fat from your belly, spin it in a centrifuge, and inject the soup into your joints. But in reality.. Does it work? Sometimes, the anti-inflammatory effect helps, but these cells do not actually regenerate the cartilage. In some cases, unproven injections can cause infections or tumors that worsen your health.
|
The Myth |
The Scientific Reality |
|
“Stem cells can cure any disease right now.” |
False. Currently, the only FDA-approved standard therapies are for blood/immune disorders (like Leukemia). Everything else is largely experimental. |
|
“Stem cells come from aborted fetuses.” |
Mostly False. Most research today uses adult stem cells or iPSCs (induced pluripotent stem cells). Embryonic research exists but is highly regulated and distinct from abortion procedures. |
| “More cells mean better results.” |
False. It’s about the right cells, not the number. Injecting millions of wrong cells can cause calcification or tumors. |
| “It’s natural, so it’s safe.” |
False. If stem cells grow unchecked, they can form teratomas (tumors composed of tissues such as teeth, hair, and bone). Control is everything. |
The Future: Organ Printing and “Banking”
The ultimate aim of regenerative medicine is to end the organ donor waiting list. Right now, if you need a kidney, you have to wait for a donor who matches your immune system, and you have to take anti-rejection drugs for your survival. In the future, doctors take a sample of your skin graft, turn it into iPSCs, and use a 3D bio-printer to build a kidney scaffold. Because the cells are yours, your body won’t reject the organ. Though scientists have successfully printed simple tissues like bladders and skin grafts, this Stem Cell Technology is a growing research area where complex structures are still being studied.
Should You “Bank” Your Child’s Cord Blood? This is a common question for parents. Cord Blood is rich in stem cells. Public donation is generally recommended over private banking. A child’s chances of using their own cord blood are extremely low (and their cord blood also carries a genetic disorder). But every year, public banks help leukaemia patients save thousands of lives.
Conclusion: The Dawn of a New Era
Stem cells are not just a buzzword; they are the basic mechanics of life. Stem Cell Biology represents a change in medicine from “treating symptoms” to “repairing the source.”
We are currently in a transition period. We have mastered the blood system, we are making strides in skin and cartilage, and we are knocking on the door of curing diabetes and neural damage.
The “Magic Clay” of the human body is real. It requires patience, rigorous science, and safety checks, but the potential is limitless. We are moving toward a future where “repairing” a human body is as standard as repairing a car. All thanks to these microscopic master builders!