Bioethics Explained: Key Ethical Principles in Biology and Medicine
You may have heard the term “bioethics” in school, a headline about science, or in a conversation about healthcare. So what does “bioethics” actually mean? In simple terms, Bioethics are ethical decisions related to life sciences and in biology and medicine ; therefore, bioethicists are concerned with how we treat living organisms. In many ways, bioethics support scientists, physicians, and policy-makers as they attempt to answer questions about the rightness or wrongness of various medical technologies, how to conduct biological research ethically, and how to ensure that both human and animal subjects are treated with dignity.
This article will provide an overview of bioethics including; its origins, the main tenets of bioethics, and the role of bioethics in biological research and medical practice; how bioethics are viewed globally; and some of the major challenges faced today, as well as a few real cases of how bioethics has impacted people’s lives, so everyone can understand why bioethics should matter to all of us, not just to scientists and physicians.
Understanding Bioethics
At its very beginning, bioethics concerns itself with the following types of questions:
- Are new drugs allowed to be tested on humans?
- Should we use animals for research purposes?
- How do we respect a patient’s choices in healthcare?
- Is it wrong or right to genetically engineer living organisms (e.g., crops)?
Although these all appear to be relatively easy questions, they usually have far more than one answer, and Bioethics gives you a means of considering the ethical implications of these types of situations.
A Simple Way to Think About Bioethics
Imagine you are a scientist working on a new medicine. You want to test it on humans to see if it works. Bioethics helps you answer questions like:
- Are the volunteers fully informed about risks?
- Could the experiment cause harm?
- Is it fair to include some groups but not others?
By following bioethics, your decisions are guided by morality, safety, and fairness, not just by scientific curiosity.
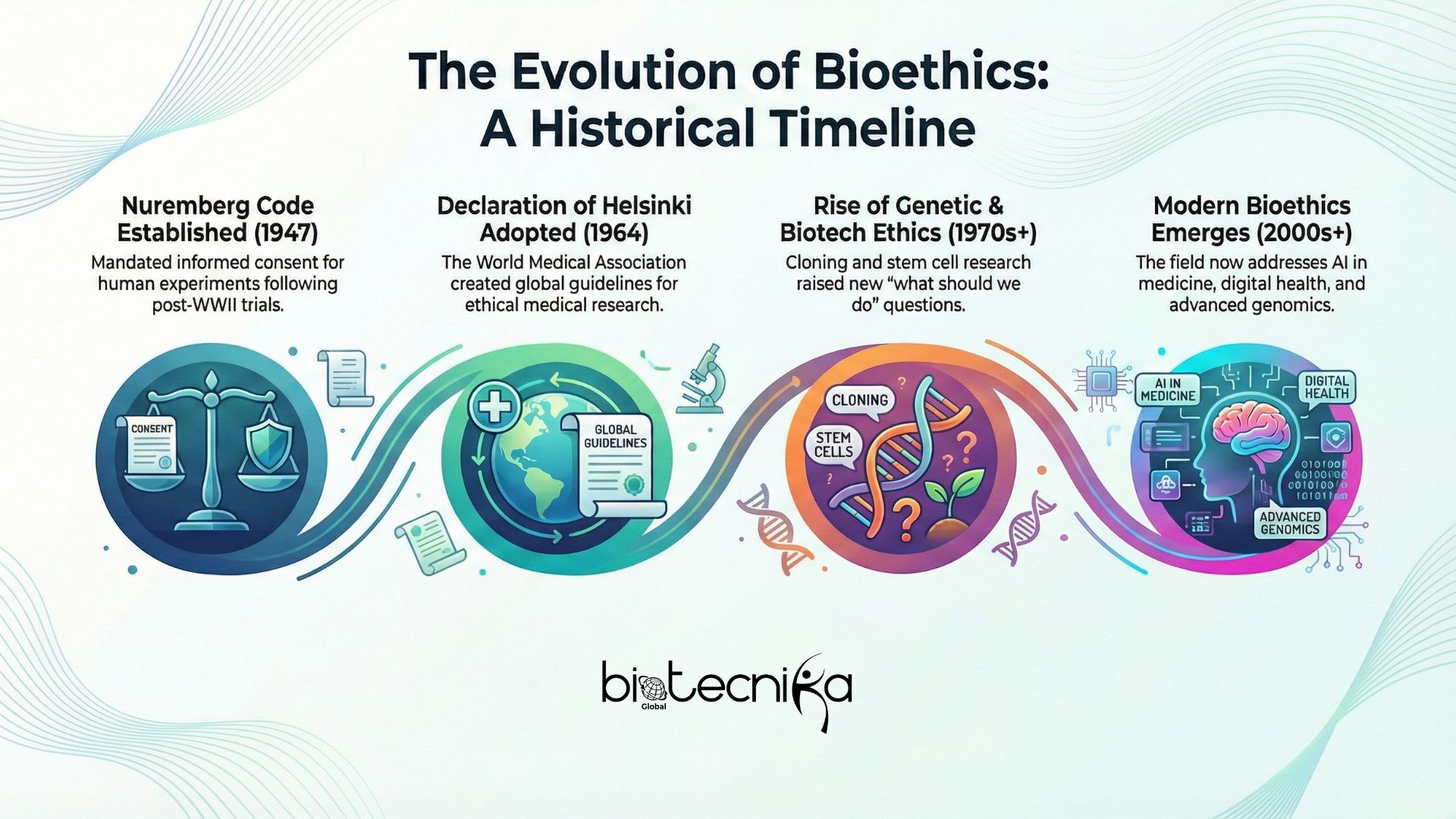
The History of Bioethics
Although bioethics has been a concept for some time now, it did not have a structured approach until the mid-20th Century. Major historic events contributing to bioethics include:
- Nuremberg Code (1947):
Doctors were tried after World War II for performing experiments without consent on prisoners. Following their trials, the Nuremberg Code was developed to stress the importance of informed consent and protecting subjects’ safety in human experimentation.
- Declaration of Helsinki (1964):
The World Medical Association developed guidelines to guide ethical conduct in medical research around the world. In the Declaration of Helsinki, special emphasis was placed on the ethical treatment of human beings as research subjects.
- Advances in Genetics and Biotechnology (1970s onward):
Genetic and Biotechnological advancements have created various opportunities (i.e., cloning, embryonic stem cell research, etc.) to raise ethical questions regarding genetic manipulation and how far science can go. As a result, bioethicists spent more time debating the “what should we do” types of questions.
- Modern Bioethics (2000s-present):
At the present time, bioethics is also addressing issues related to Artificial Intelligence in Medicine, Digital Health Records, and Advanced Genomic Testing. These current developments and issues indicate that bioethics continues to grow and develop with the advancement of science.
Principles of Bioethics
To guide ethical decision-making, experts developed core principles of bioethics. Think of them as a compass that points to the right path.
| Principle | What It Means | Example in Biology and Medicine |
| Autonomy | Respecting a person’s choices | A patient decides on their treatment plan |
| Beneficence | Acting for the benefit of others | Doctors giving treatments that improve health |
| Non-Maleficence | Do no harm | Avoiding procedures that can cause unnecessary risk |
| Justice | Treat everyone fairly | Ensuring equal access to medical care |
| Respect for Life | Valuing all living beings | Ethical treatment of animals in research |
These principles of bioethics ensure that biology and medicine are practiced responsibly and ethically.
Bioethics in Biological Research
Biological research usually includes doing experiments, testing, and collecting data. Many of the scientific advancements that come from biological research have the potential to create ground-breaking findings, but they also create ethical dilemmas.
The following are examples of some ethical issues related to biological research:
- Can we clone animals or people?
- Are we allowed to create genetic modifications?
- How do we ensure that we protect human volunteers who participate in clinical trials?
Bioethics provides guidelines for conducting biological research that respects the dignity of humans and animals and maintains sustainable practices for the environment. Bioethics helps scientists reflect upon the question: “Just because we can, does it mean we should?”
Ethical Checkpoints in Biological Research
| Step in Research | Ethical Question | Example |
| Planning an experiment | Are participants safe? | Clinical trials for a new drug |
| Using animals in research | Are animals treated humanely? | Lab mice kept in proper conditions |
| Genetic modifications | Could this harm future generations? | Editing genes in embryos |
| Publishing results | Are findings reported honestly? | Avoiding falsified research |
Following these checkpoints ensures that biological research benefits humanity without causing harm.
Bioethics in Biology and Medicine
The importance of bioethics in healthcare cannot be overstated. Each day, doctors, nurses, and other healthcare professionals are faced with ethical choices regarding patients and their care, often under pressure from either their employer or the demands placed upon them by the patient or family members.
Here are some examples:
- Patient Consent: When a patient has provided his or her consent for a particular treatment to take place, then the healthcare professional can proceed knowing that he or she has been provided with the necessary information for making an informed decision.
- End-of-Life Care: Another important aspect of bioethics focuses on determining the appropriate course of treatment when a patient is nearing the end of life. Healthcare providers must consider all possible options for prolonging life and providing comfort to the patient while respecting the patient’s wishes.
- Medical Research: In regard to research, the process of testing new medications involves obtaining ethical authorization before commencing with any testing, as well as ensuring that extensive records are maintained regarding all aspects of the study, including results and any adverse reactions experienced by patients.
- Privacy and Data: As electronic health records have become widely utilized, there is an increased need to maintain the confidentiality of patient information.
Bioethics also allows for balancing issues relating to patient rights, the benefits of medicine, and the fairness of the healthcare system.
Global Perspectives on Bioethics
It is difficult to find bioethical principles defined in exactly the same manner from one culture, religion, or society to the next. In many countries, the focus of bioethics is to protect and promote the welfare of the community, while in other countries, the focus is on protecting the rights of the individual.
There are a number of international guidelines available that can provide a framework for developing global ethical standards such as the Declaration of Helsinki.
The core principles of bioethics, regardless of differences between cultures, all share a commitment to the same basic values: autonomy, beneficence, non-maleficence, justice, and respect for life.
Bioethics Across the World
| Region | Ethical Focus | Example |
| North America | Individual rights | Patient autonomy in treatment |
| Europe | Balanced approach | Strict clinical trial regulations |
| Asia | Community welfare | Public health policies during epidemics |
| Global | International standards | WHO guidelines on human research |
Famous Cases in Bioethics
- Henrietta Lacks (1951):
In 1951, Henrietta Lacks’ cells were taken from her without permission, leading to many discussions about patient rights and informed consent issues in biological research.
- Tuskegee Syphilis Study (1932–1972):
From 1932 to 1972, the Tuskegee Study involved a group of African-American men who were not informed about what type of treatment they received concerning syphilis.
- CRISPR Gene Editing:
The use of CRISPR to edit genes is still being debated by scientists and bioethicists who want to know if the practice is safe or ethical to perform on embryos.
- Animal Testing in Medicine:
There has been significant research on animals that has resulted in life-saving treatments for humans; however, there are ethical questions about how the animals involved in research are treated and a desire to find a viable alternative to animal use whenever possible.
In summary, each of these cases demonstrates that bioethics isn’t just theoretical. It has a significant impact on individual human beings, as well as their animals and the results of their research.
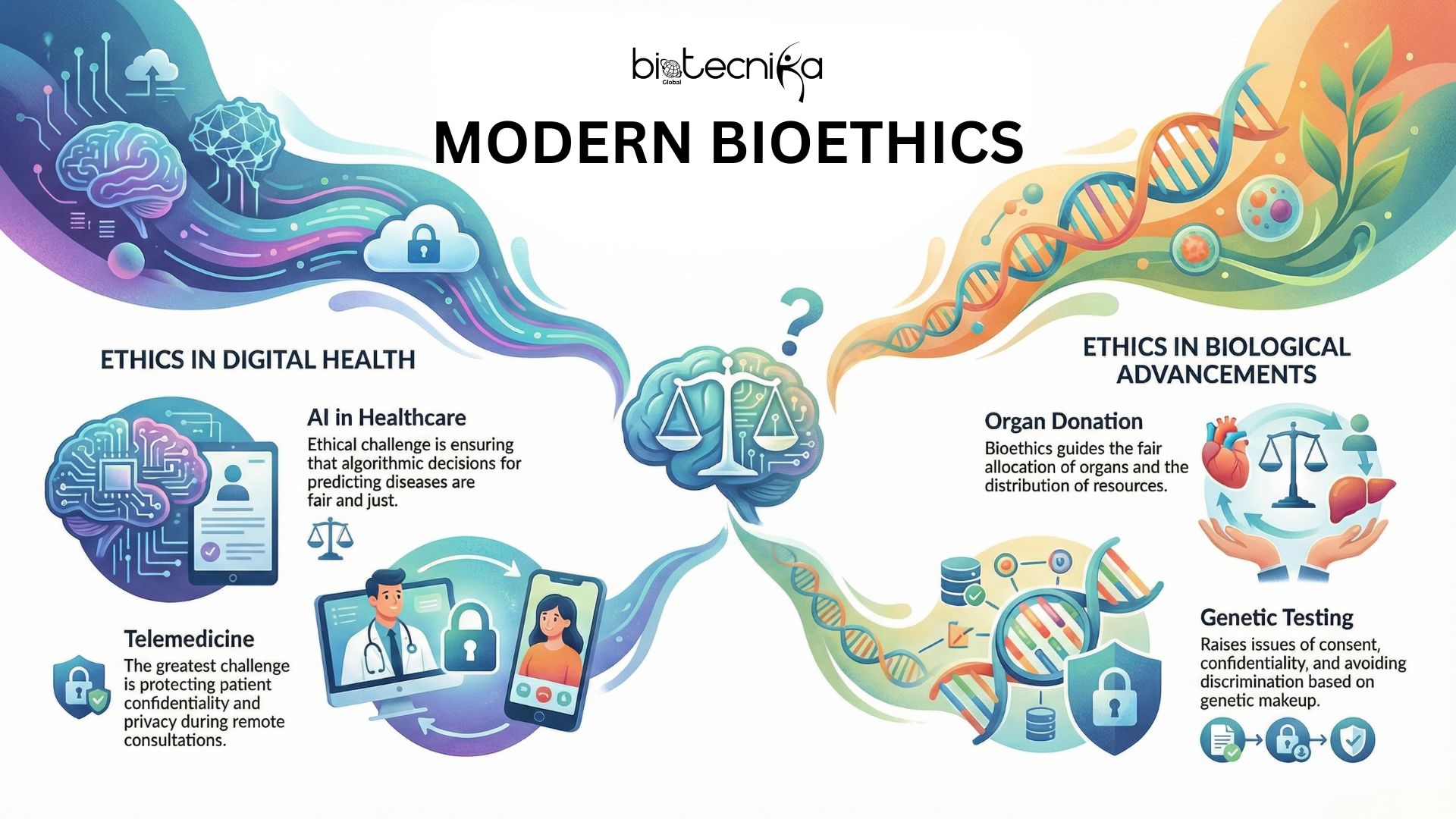
Modern Applications of Bioethics
Bioethics is becoming more important as science and medicine advance. Some modern examples includes:
- AI in Healthcare: Algorithms can predict diseases, but the decisions that we take must be ethical and fair.
- Telemedicine: The greatest challenge associated with the use of telemedicine, or providing remote medical consultations via the Internet; is protecting patient confidentiality and privacy.
- Organ Donation: Bioethics is the ethical framework that is guided by the principles of bioethics on how organs are allocated to patients and how resources to distribute those organs are used.
- Genetic Testing: Many tests are now available to individuals to use in assessing their genetic risk for developing a disease or trait. This process raises multiple ethical issues including: maintaining confidentiality, obtaining informed consent, and avoiding discrimination against individuals with certain genetic makeups.
All of these examples illustrate that bioethics is not a static body of knowledge, rather bioethics continues to evolve along with advancements in science, technology, and society.
Challenges
Even with clear principles, bioethics faces challenges:
- Technological Advances: Rapid progress in genetics, AI in healthcare, and biotechnology creates new dilemmas.
- Resource Allocation: How do we fairly distribute limited medical resources?
- Cultural Differences: Ethical standards vary, making global consensus difficult.
- Informed Consent: Ensuring participants understand risks is not always simple.
- Environmental Impact: Biological research can affect ecosystems, so ethical responsibility extends beyond humans.
Why Everyone Should Care About Bioethics
Bioethics is not just for scientists or doctors; it affects all of us:
- When you take medicine or receive treatment, bioethics ensures safety.
- When society debates genetic engineering, organ donation, or vaccines, bioethics guides decisions.
- When governments make public health policies, bioethics ensures fairness and responsibility.
Understanding bioethics helps us make informed decisions and participate in important discussions about biological research and biology and medicine.
Fun Facts
- The term “bioethics” was first used in 1970 by the American biochemist Van Rensselaer Potter.
- Henrietta Lacks’ cells are still used in research today.
- Many bioethics debates involve balancing life-saving treatments with quality of life.
- Ethical boards called IRBs review research studies to protect participants.
- Stem cell research is highly debated due to ethical concerns.
- Animal ethics committees ensure humane treatment in labs.
- Global guidelines exist to prevent unethical medical practices.
- Bioethics is taught in schools and universities worldwide.
- AI in medicine is a new ethical frontier.
- Ethical dilemmas in biology and medicine often inspire movies and books!
Conclusion
The connection between science and society is demonstrated through bioethics. The field of bioethics ensures that biology and medicine are practiced responsibly, safely, and fairly. By following the principles of bioethics, we can respect human rights, preserve life and provide sound guidance to researchers regarding the conduct and direction in which biological research is headed.
Students, researchers, health care professionals, and citizens alike all benefit from learning about bioethics as it provides them with insight into how the impact of biology and medicine on their present and future lives.
Key Takeaways:
- The study of bioethics examines the ethical aspects of biology and medicine
- Principles of bioethics provide a framework to make ethical decisions in a fair and safe manner.
- Balancing progress with responsibility is a key component of effective biological research.
- Bioethics has a broad application, it is not limited to individuals that hold advanced degrees in the fields of biology or medicine.
By learning and applying bioethics, we can ensure that science benefits humanity without crossing ethical boundaries.