Proteomics: A Comprehensive Approach to Protein Function in Complex Biological Systems
Have you ever wondered how life actually works at the molecular level? Well, most of the life science students and researchers have the same question too. While genomics studies reveal the mysteries of our DNA, do you think that’s the whole story? What if I tell you that the real story is hidden a level deeper? Yes, the machinery of life that drives our system is hidden in the proteins. And the study of these hidden mysteries is called Proteomics.
What if you can see and understand these proteins in action? Imagine exploring their interactions, modifications, and roles in the complex biological systems; that’s exactly what proteomics is. By decoding entire proteomes, researchers are now uncovering the hidden mechanisms underlying our health and disease, and even the potential of personalized medicine.
Here, we will explore what proteomics is, the latest technologies, and its transformative applications across medicine, agriculture, and systems biology. By the end of this, you will be able to understand why proteomics is not just a field of research. But a revolutionary lens for understanding life itself.
What Is Proteomics?
To explore this field further, you first need to understand what proteomics is. Well, its a systematic analysis of Proteomes. These Proteomes are the complete sets of proteins that are produced by a biological system under specific conditions. While the genome is remains relatively constant, proteomes are highly dynamic and change. These changes can be a response to development, environmental stimuli, disease states, or therapeutic interventions.
Due to this dynamic nature, proteomics is a unique and powerful field of science. A single gene can give rise to many different proteins. This can be done through alternative splicing and post-translational modifications such as phosphorylation, glycosylation, and acetylation.
Because of this, the proteome contains more proteins than the number of genes in the genome. Studying proteins directly is therefore important to understand phenotype, cellular behavior, and how biological systems function.
What is the difference between Proteomics and Genomics Studies?
Do you know that genomics studies are all about DNA and gene expression? But they do not completely explain how cells actually work. That’s where Proteomics, the study of proteins, came into play. It helps us fill in the gaps that genomics misses.
Let’s understand this more clearly. While genes are like instructions, proteins are the ones that do the real work. They build cell structures, speed up chemical reactions, send signals, and control many processes in our bodies.
The amount of protein in a cell does not always match how many mRNA are made. Many proteins are regulated after translation. Protein–protein interactions, subcellular localization, and structural changes influence the function of a protein. These details are best studied through proteomics.
When proteomics is combined with genomics and transcriptomics, scientists get a bigger picture of how life works at the molecular level.
What are the major Types of Proteomics Approaches?
There are many different approaches in this field. Each one helps our scientists understand proteins in a more detailed way.
-
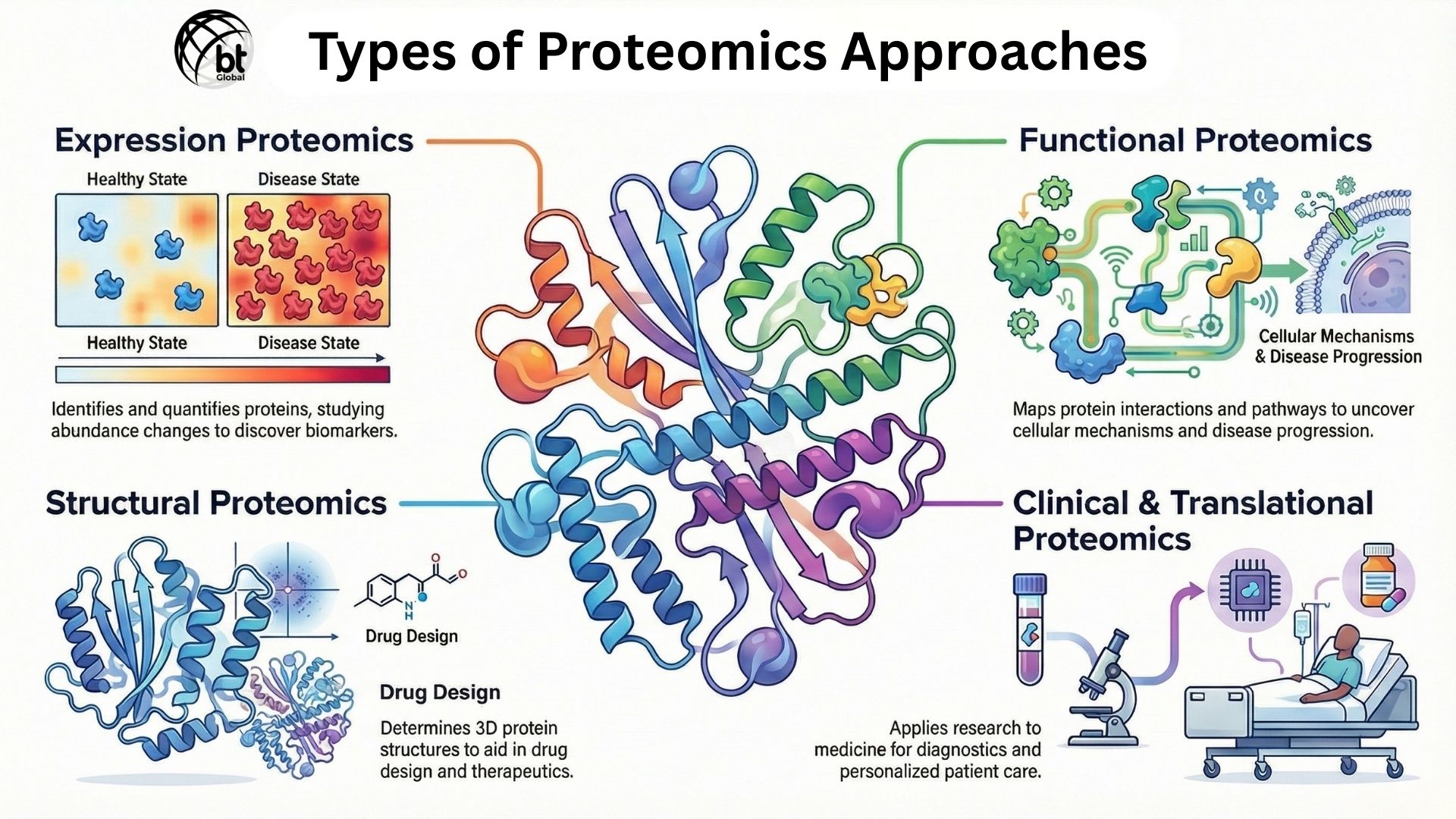
Expression Proteomics
In this approach, we look at proteins that are present and how each protein will behave under different conditions. For example, it compares healthy tissue to diseased tissue to find proteins linked to illness. These proteins can become useful disease markers.
-
Functional Proteomics
Whereas in Functional proteomics, we investigate how proteins interact and function within a cellular network. This can be understood by protein-protein interaction mapping and signaling pathways. With this approach, researchers can learn more about mechanisms that regulate cell behavior and disease progression.
-
Structural Proteomics
With Structural proteomics, we can determine the 3D structures of proteins and their complexes. These structural insights are important to understand protein function. This will also be widely applied in rational drug design and molecular therapeutics.
-
Clinical and Translational Proteomics
This approach turns research into medical applications. It plays an important role in biomarker discovery and diagnostics. We can use this for developing personalized and precision medicine strategies.
What are the important Technologies Used in Proteomics?
| Technology | What it does |
| Mass Spectrometry (MS) | This is the main tool used in proteomics. It helps scientists find and measure many proteins from complex samples. |
| LC-MS/MS | This method separates proteins first and then identifies them. It is the most commonly used technique in proteomics labs. |
| Two-Dimensional Gel Electrophoresis | This technique separates proteins based on size and charge. It is still useful for certain types of studies. |
| Quantitative Proteomics | This approach measures how much of a protein is present. It can use labels like SILAC and TMT or work without labels. |
| Bioinformatics | Computer tools are used to handle large amounts of data, identify proteins, and study biological pathways. |
| Protein Databases | Databases like UniProt and resources from HUPO store important protein information that researchers rely on. |
How Do Scientists Use Proteomics to Study Living Things?
The study of proteins is one of the most powerful areas in terms of the ability to uncover the codes in the complexity of Biological Systems. Cells function in a way that is networked in relation to proteins and not in terms of molecules that are isolated. Through this area, one can map the networks of a cell. Additionally, we get to understand the way proteins coordinate cell functions such as metabolism, immunity, and growth.
Proteomics provides systems-level information on how biological functions take place by analyzing protein dynamics, post-translational modifications, and interaction networks. This approach has been very useful in advancing Biological Systems. Understanding protein interactions and feedback mechanisms is as important as identifying individual components.
How Do Scientists Use Proteomics in Life Science?
-
Biomedical and Disease Research
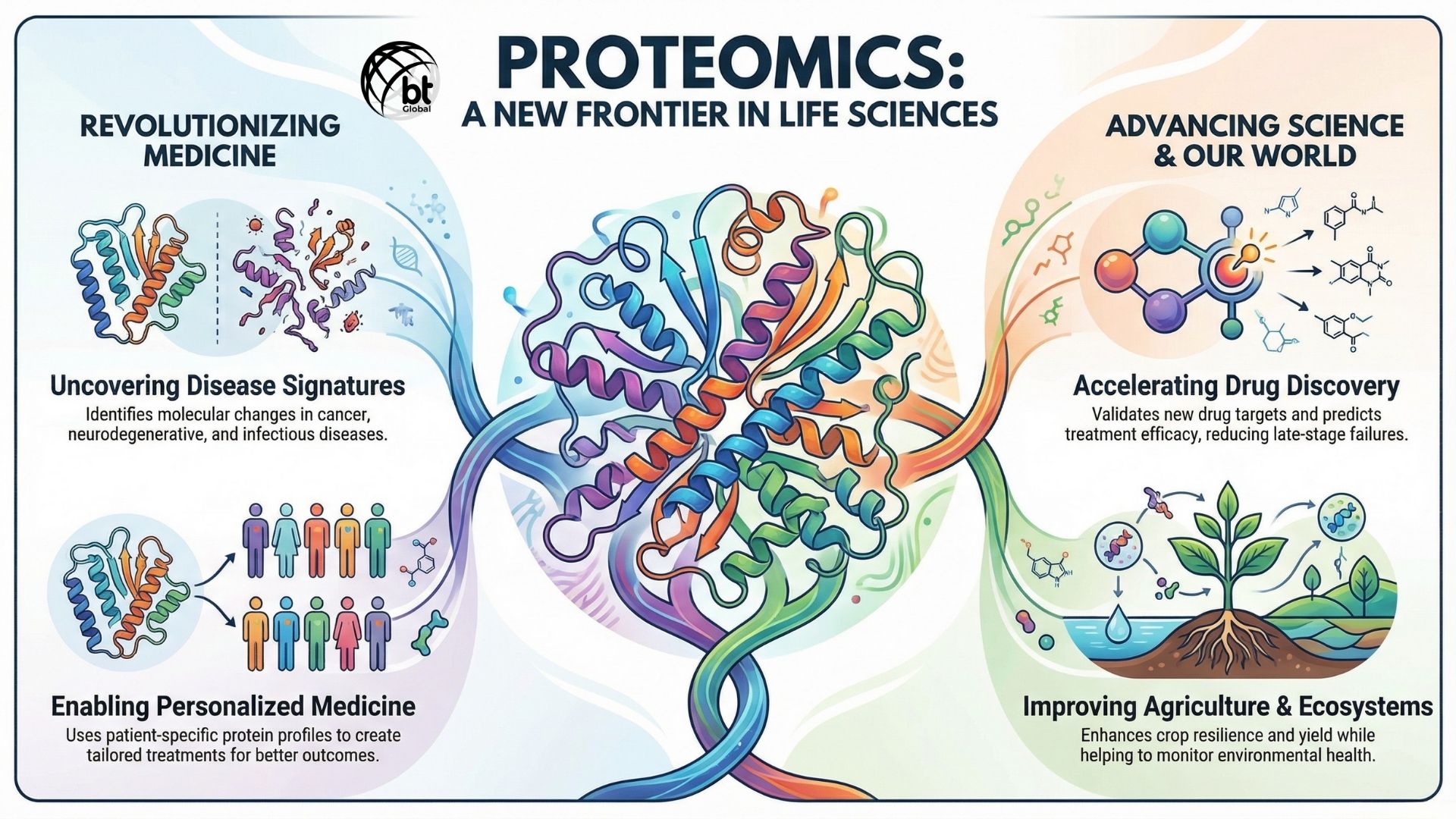
With Proteomics we can now understand diseases at the molecular level. When we talk about cancer research, this field reveals the altered signaling pathways. It also helps in identifying novel therapeutic targets. This can also be used in neurodegenerative disorders. It explains the mechanisms of protein aggregation and misfolding. It also plays an important role in infectious disease studies by analysing host-pathogen interactions.
-
Drug Discovery and Development
Proteomics speeds up drug development by enabling target identification, validation, and toxicity testing in pharmaceutical research. The researchers can better predict efficacy and adverse effects by studying how drugs interact with proteins. This helps reduce failures of developed drugs in the late stages.
-
Agricultural and Environmental Sciences
Apart from medicine, this field also have wide range of applications in agriculture. Some of them are improving crop resilience, yield, and stress tolerance. Environmental proteomics helps scientists monitor ecosystem health and understand how organisms respond to environmental changes.
-
Personalized and Precision Medicine
Proteomics is the basis for personalized medicine. Doctors can provide treatments based on molecular characteristics by profiling patient-specific proteomes. This improves outcomes and reduces unnecessary interventions.
What are the Challenges and Limitations in Proteomics?
| Challenge | Explanation |
| Protein complexity | Cells contain thousands of proteins, and their amounts can vary a lot, which makes analysis difficult. |
| Sample preparation | Preparing samples correctly is tricky and can affect the final results. |
| Reproducibility | Getting the same results every time can be hard, especially across different labs. |
| Lack of standard methods | There is no single standard approach, which makes comparing studies difficult. |
| Data analysis | Proteomics generates large amounts of data that require powerful computers and reliable databases for analysis. |
| High cost | Advanced instruments are costly. Also, they are not always available, especially in low-resource settings. |
| Limited accessibility | Not all labs can access the latest technology due to cost and infrastructure needs. |
| Ongoing improvements | New technologies are slowly helping to reduce these problems and improve results. |
What are the Recent Advances and Future Trends in Proteomics
The world is moving faster than ever, and so is proteomics. Now, with the help of single-cell and spatial proteomics, we can learn about protein expression like never before. We can also explore cellular heterogeneity in the tissues.
The advancing technologies like AI and machine learning have also boosted the growth of this field. With these advanced technologies, we can analyse complex biological data and also predict protein structure and interactions.
When we look at life science research across the world, we can see an increasing shift towards multi-omics research. This integrating proteomics shift is with genomics, metabolomics, transcriptiomic and epigenomics. The importance of this field is further rising as global efforts to map complete human proteomes make headway.
Why Proteomics Is Essential for Modern Biology?
This growing field of science is filling up the gap in life science research by directly measuring functional molecules. It also provides us insights that we can’t gether with genomics studies alone. It plays an important role in understanding health, diseases, and biological complexity.
With the advancing technologies, this field is growing too. It is improving and integrating across different fields of science. Today, proteomics is shaping the future of biological and medical research across the world.
FAQs
1. What is proteomics, and why is it so significant?
It is the study of many proteins in our body. This helps us know how our bodies function and how an illness occurs. There is also something called proteomics testing. This is typically what doctors rely on when looking for an illness
2. How do proteomes differ from genomes?
Genomes remain fairly similar. But proteomes vary every day based upon what’s happening in our body, or in the case of someone who might be ill.
3. What role does proteomics play in genomics?
Genomics explains our genes, while proteomics explains what happens in our bodies because of our genes, like the function of proteins or how proteins interact with each other.
4. What are the tools for proteomics?
There are various methods employed by scientists in the process of understanding proteins, such as mass spectrometry, chromatography, and computer
5. In what ways is proteomics applicable in the medical sector?
It can be used to look for indicators of illness, to discover the creation of new medications. And to determine the course of treatment that would be most effective for each individual.