Understanding Global Clinical Trials: From Planning to Approval
Thanks to Clinical Trials, Improvements in Medical Sciences Enhance our Lives. Clinical trials are major contributors to many improvements in medical science/healthcare systems around the globe. In fact, all medications, Vaccines and medical treatments that Doctors administer to patients must go through extensive clinical research to verify their quality assurance, safety, and effectiveness prior to receiving approval for distribution. Thus far, these trials are the basis of evidence-based medicine utilized by health care providers throughout the world.
However, although the overall objective of conducting clinical trials is universal (e.g., to improve the quality of care provided), the factors that influence how and or why these trials are performed will vary according to individual nations’ laws & regulations (i.e. by providing these trial Sponsors with institutional and/or governmental approvals), differing healthcare systems or models between countries.
This article will describe how clinical trials work, the phases of a trial, and how/why regulations concerning the conduct of the trial are different in various locations around the globe.
What Is a Clinical Trial?
Clinical trials, or Clinical Research Studies, are scientific studies done on humans to test new drugs and medications. In these types of studies, researchers observe how the human body reacts and whether there are any adverse or side effects from a new treatment. Without these trial, physicians would have no way of knowing if the new treatment is safe.
This process will begin with laboratory testing in animals and then go on to human testing once researchers feel confident with the information obtained from the animal trials. Global clinical research and trials allow researchers to gain additional insight into how well their treatments are working; this is especially true when medications are being used on a variety of different nationalities of people.
Why Are Clinical Trials Important Worldwide?
This process helps doctors in discovering better treatments for diseases. They also safeguard candidates from using harmful medications. Internationally, global clinical research and trials is crucial, as individuals in various geographical areas may react differently to the same drug.
An international clinical trial also helps speed up the research by conducting it in different countries concurrently. The final result is an improved procedure for conducting these trials process and quicker access to new medicines for patients who require them.
Clinical Trial Phases Explained Simply
Every clinical trial is divided into steps known as clinical trial phases. Each phase has a clear purpose and builds on the previous one.
Overview of Clinical Trial Phases
| Phase | Purpose | Number of Participants |
| Phase 1 | Tests safety and dosage | Small group (20–100) |
| Phase 2 | Checks effectiveness | Medium group (100–300) |
| Phase 3 | Compares with existing treatments | Large group (1,000+) |
| Phase 4 | Long-term monitoring after approval | Ongoing |
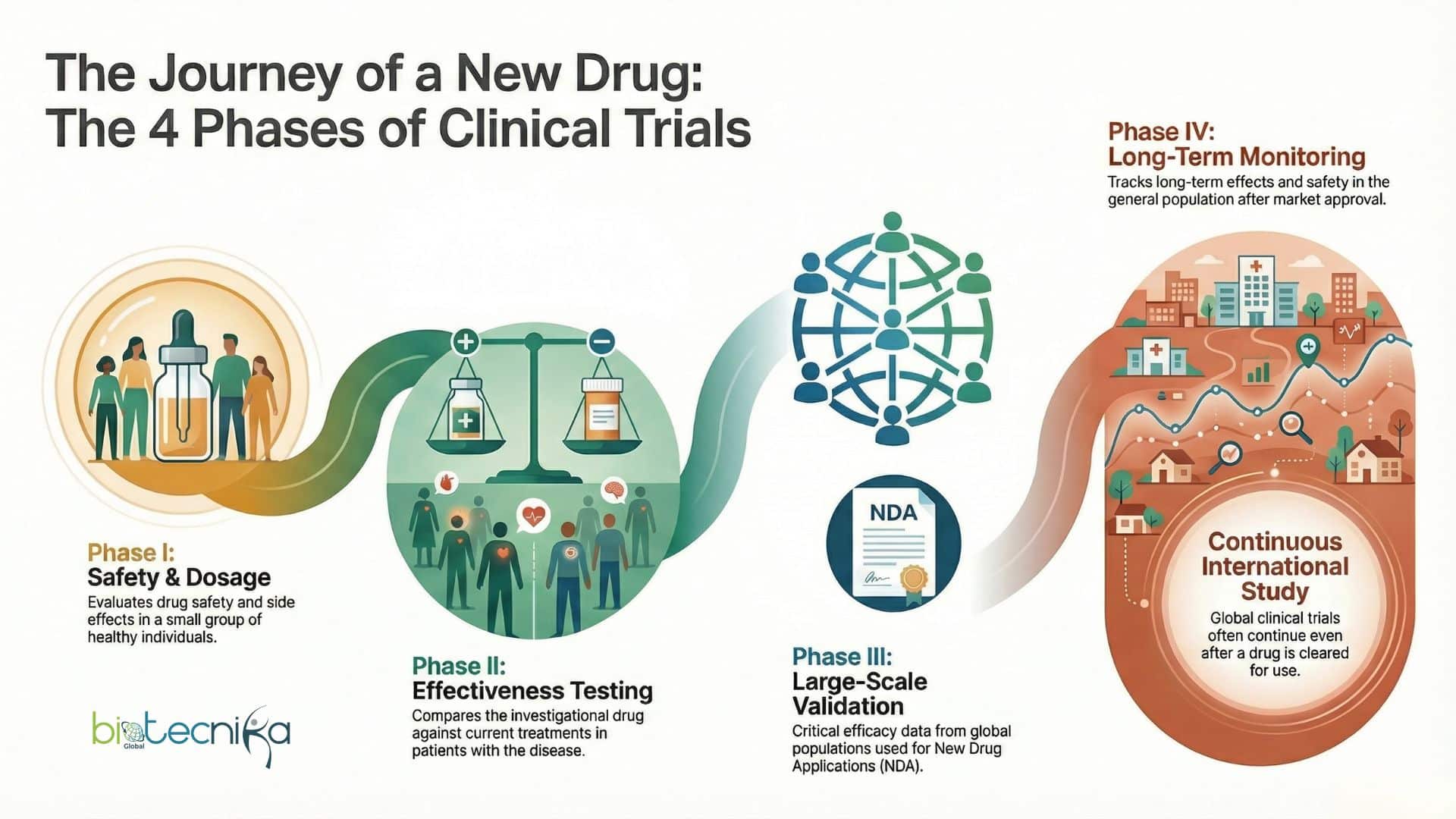
Phase 1
In the initial stage, Phase I of the trial process, the researcher will evaluate the safety of the investigational drug by administering it to a group of healthy individuals and collecting data regarding the drug dosage and any associated/product side effects.
Phase 2
During Phase II, patients suffering from the target disease are administered the investigational drug and the researcher tests the effectiveness of the investigational drug versus the patient’s current treatment while continuing to collect data regarding the safety and side effects of the investigational drug.
Phase 3
Phase III is very significant in the overall new drug application (NDA) process because it is at this time that the efficacy of the investigational drug is evaluated in a much larger patient population. The NDA will be evaluated based on the Phase III trial data, as long as the phases have been done properly according to FDA standards and guidelines. During Phase III, the majority of global trial programs happen.
Phase 4
Phase IV, the test begins after a drug has been approved for marketing and provides additional information regarding the long-term effects of the drug on all patients. Several international trial studies evaluating the investigational drug will continue even after approval for marketing/safe use of the drug has occurred.
The Global Clinical Trial Process
The entire process is generally the same all over the globe. Researchers begin by developing their protocols or study plans before submitting them to ethics boards for approval. After the protocol is approved, volunteers will be enrolled from all participating countries.
In an international trial, the same rules must be adhered to by teams from different countries, ensuring the data is as comparable as possible across all sites involved. In addition, technology will enable the successful management of the global clinical trial process to proceed without interruption.
Clinical Trial Regulations Around the World
Every trial must follow legal and ethical rules known as clinical trial regulations. These rules protect participants and ensure honest research.
Clinical Trial Regulations by Region
| Region | Regulatory Authority | Key Focus |
| United States | FDA | Patient safety and data accuracy |
| Europe | EMA | Ethical approval and transparency |
| India | CDSCO | Ethics, consent, and safety |
| Japan | PMDA | Quality and clinical data |
Different l regulations exist across regions. A global trial must follow all local rules. This makes planning complex but ensures safety in every trial.
Regional Differences
While there are similarities between these trial processes across all areas of the world, there are definitely differences depending on where you are conducting the study.
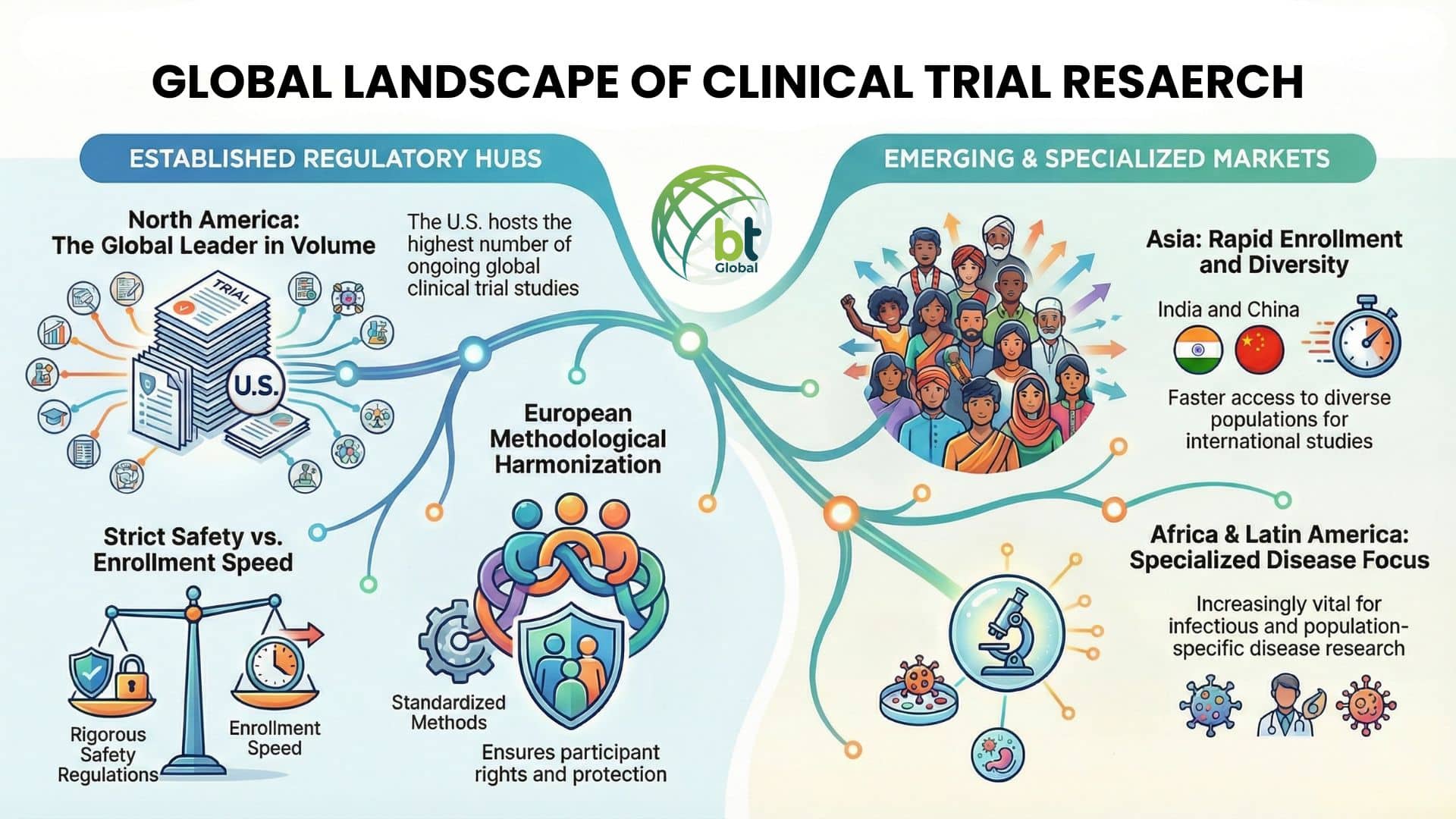
North America
The U.S., in particular, has the highest number of ongoing global clinical studies. The U.S. has strict regulations when it comes to conducting the trials to ensure subject safety; however, one drawback is the long time frame to gain access to subject enrollment in clinical studies.
Europe
Europe contributes to the global effort of conducting international clinical research via harmonization/standardization of clinical research and trial methods and participant rights during the phases to ensure all trial participants are protected.
Asia
More countries in Asia are participating in international clinical trial studies than ever before, particularly India and China, because they provide faster access to enroll subjects and a greater diversity in their populations.
Africa and Latin America
The importance of Africa and Latin America is increasing with respect to conducting global clinical trial research, in particular for the regions that have issues with infectious diseases or have population-specific diseases.
Challenges
Conducting a clinical trial is complex. These problems may delay the trial due to language barriers, cultural variations, and country-specific differences in their regulations.
For a successful global trial, consistent communication and effective planning will be required. All trial sites will need to fully understand the process for conducting an international trial in order to ensure that high standards are met for the entire trial.
Benefits of International Clinical Trials
A global clinical trial provides better data by including people from different backgrounds. This also helps share medical knowledge worldwide.
Patients benefit from early access to treatments. Doctors learn faster. Overall, the process becomes more effective.
The Future
Technology is improving the system of clinical research and trials. Online monitoring and digital tools are making the process faster and easier.
In the future, global clinical trial programs may become more patient-friendly. Better coordination of the regulations could reduce regional differences.
Conclusion
There is a critical need for trials to create safe and effective therapies. Patient safety is always the primary concern, regardless of whether the trial is local or international. By learning about the trial phases, clinical trial regulations surrounding the trials, and the operation of the clinical trial process, we can gain a deeper understanding of how modern medicine has developed. As we continue to establish more international trial activity, our healthcare systems will improve around the globe.



