Precision Medicine: How DNA is Shaping Personalized Healthcare
Imagine an environment where doctors prescribe unique medicines to their patients – Personalized Medicine. Rather than doling out the same drugs to everyone. Rather than being fiction, this is precisely what’s produced through precision medicine! Precision medicine is a healthcare model where therapies are designed according to a person’s genetic composition (e.g., DNA, genetic information) – Pharmacogenomics. The way of their life (e.g., diet, fitness, lifestyle), and their surroundings (e.g., where they live). The objective of providing healthcare is to develop a more intelligent way of giving treatment.
Traditionally, most physicians determined the pharmaceuticals to be prescribed based solely upon patients’ symptoms. However, we are all unique and therefore respond differently to medications. While the therapy seems to work beautifully for one patient, it may not do anything at all for another. In the worst case, it may cause adverse reactions. Through the scientific use of precision medicine, physicians are capable of customizing drug therapy. This thereby creating a greater potential of successful treatment for everyone.
What is Precision Medicine?
Precision medicine is a new way of thinking about how to provide health care service. It’s not assuming that “one size fits all”. It considers the individual characteristics of a patient to create a customised health care service. The characteristics of an individual include:
- Genetics: The instructions in your DNA define how well you will respond to medications.
- Lifestyle: What you eat, how you exercise and how you live your life will all play a role in how well your medication works.
- Environment: The air you breathe, the amount of stress you have and the toxins you come into contact with can all influence your health.
By taking all of these factors into account, doctors can develop a personalised medicine approach. This seems to be much more likely to succeed. Simply stated, precision medicine is like having a key made specifically for your unique health issues.
How Precision Medicine Works
A fundamental element of precision-based medicine is understanding your genetic makeup. Human DNA contains many genes that help to define who we are as an individual. Those those genes can also influence how we process medications and how they will affect us. A doctor will analyse a person’s genes to see what medicines are going to work for them. Or if they will have side effects from taking those medicines.
Pharmacogenomics is one of the primary avenues of precision medicine. The study of pharmacogenomics enables scientists and physicians to predict which medicines will be the safest and most effective. This is based on an individual’s unique genetic background.
For instance, two patients can suffer from the same medical condition, but require a different treatment regimen. A physician can use personalised medicine to determine what medication and at what dosage would be optimal for that specific patient. This will lead to a decrease in the number of trials and errors. When it comes to prescribing pharmaceutical products, as well as having improved treatment outcomes for those patients.
The Role of Pharmacogenomics
Pharmacogenomics uses genetic information to determine the best medication options for patients. It answers questions such as:
- Will this medication work for me?
- Can this medication cause bad side effects?
- What is a safe and effective dose for me?
Pharmacogenomics allows health care providers to provide targeted therapies with fewer side effects to patients. And this helps physicians make more informed treatment decisions. Therefore, it supports the practice of Precision Medicine.
Pharmacogenomics has revealed significant benefits in several areas; for example:
- Cancer Treatment: Drug therapies can be targeted to specific mutations in a patient’s tumor site.
- Mental Health: Certain antidepressant medications and antipsychotic medications are prescribed based on the patient’s genetic makeup.
- Genetic Disorders: There are now effective treatment options available for patients with specific genetic mutations.
Traditional Medicine vs Precision Medicine
| Feature | Traditional Medicine | Precision Medicine |
| Approach | One-size-fits-all | Tailored to individual DNA and lifestyle |
| Drug Selection | Based on symptoms | Based on genetic profile (pharmacogenomics) |
| Side Effects | Higher risk | Reduced risk with personalized treatments |
| Effectiveness | May vary widely | Higher success rates |
| Prevention | Limited | Can identify risks early for preventive care |
| Cost | Often lower upfront | Can be higher initially, but cost-effective long-term |
| Treatment Speed | Slower due to trial and error | Faster and more accurate |
Benefits of Precision Medicine
The advantages of precision medicine are significant. Here’s why it’s a game-changer in healthcare:
- Better Treatment Outcomes: Drugs designed for your DNA work more effectively.
- Fewer Side Effects: Personalized treatments reduce the risk of harmful reactions.
- Faster Recovery: The right medicine from the start speeds up healing.
- Preventive Care: Genetic testing can identify disease risks early.
- Cost Savings: Reduces spending on ineffective treatments.
- Targeted Therapy: Especially in cancers and rare diseases, treatments hit the disease directly.
- Empowered Patients: People understand their health better and participate in decision-making.
Real-Life Examples of Precision Medicine
Precision medicine is no longer just a theory; it’s happening now. Here are some examples:
- Breast Cancer: Some patients receive drugs targeting specific genetic mutations in tumors, increasing survival rates.
- Mental Health: Genetic tests help psychiatrists choose antidepressants or anxiety medications that suit the patient’s DNA.
- Cardiovascular Diseases: Certain blood thinners and heart medications are prescribed based on genetic analysis, reducing complications.
- Rare Genetic Disorders: Treatments can correct the exact gene mutation causing a disease, improving life quality.
These examples show how personalized medicine can transform treatment; from generic to highly individualized.
Challenges in Precision Medicine
While precision medicine offers huge potential, it also faces challenges:
- Cost: Genetic tests and specialized drugs can be expensive.
- Data Privacy: Genetic information is sensitive and must be protected.
- Access: Advanced treatments are not available to everyone equally.
- Limited Knowledge: Scientists are still learning how genes interact with drugs.
- Regulation: Policies need to catch up with rapid medical advances.
Despite these challenges, the field is growing rapidly. Research funding, technological advances. This is increasing awareness and making personalized medicine more accessible.
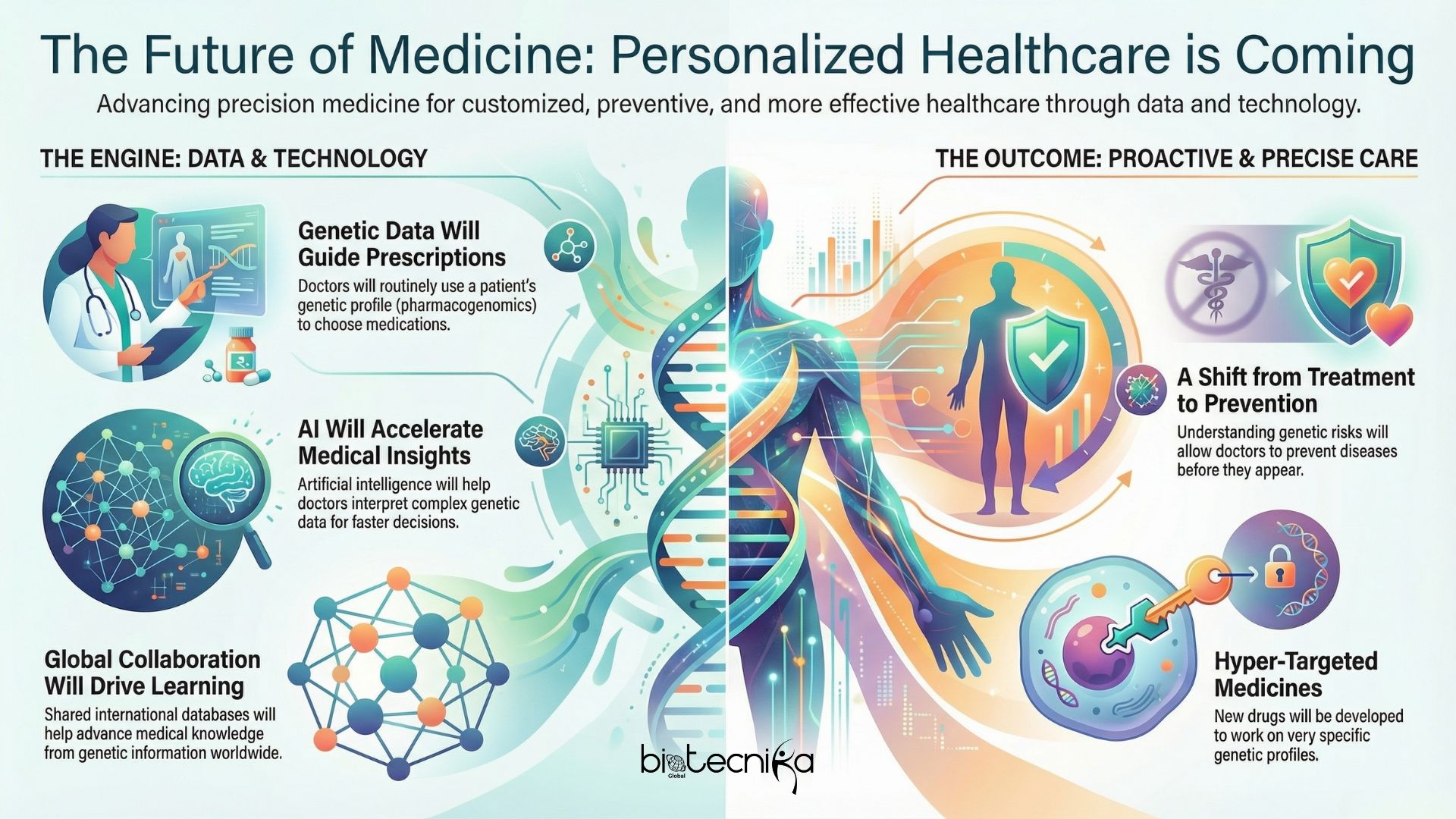
The Future of Medicine
The future of healthcare is closely connected to precision medicine. Here’s what we can expect in the coming years:
- Wider Use of Pharmacogenomics: Doctors will routinely use genetic information to guide prescriptions.
- Digital Tools for Doctors: AI and advanced software will help interpret genetic data for faster decisions.
- Targeted Drugs: Medicines will be developed for very specific genetic profiles.
- Preventive Healthcare: Instead of treating diseases after they appear, we can prevent them based on genetic risks.
- Global Collaboration: International databases will help doctors learn from genetic information worldwide.
Imagine a world where each patient has a fully customized treatment plan. Diseases could be prevented before they happen. Treatments would be safer, faster, and more effective. That’s the promise of precision medicine.
How You Can Benefit from Precision Medicine Today
Even if you are not a scientist or doctor, you can take advantage of precision medicine:
- Ask About Pharmacogenomics Testing: These tests can guide treatment decisions.
- Consider Genetic Counseling: Especially if there’s a family history of diseases.
- Stay Updated: Follow news about personalized medicine breakthroughs.
- Participate in Research: Clinical trials help expand knowledge and access.
- Adopt Healthy Habits: Lifestyle choices still influence how your body responds to medicine.
Being proactive about your health has never been easier with precision medicine.
Conclusion
Healthcare is on the verge of being transformed through the advancements in precision medicine. The combination of genetic information, pharmacogenomics, and personalized medicine. This creates a more individualized approach to treating patients by providing them with safer, better, and more personal treatments.
The field of precision medicine still has several obstacles to overcome. Including the costs associated with treatment, the protection of the patient’s private information. Providing access to everyone, but the possibilities for the future are enormous. In the future, all patients will have access to a treatment plan created for their unique needs. This will allow physicians to treat patients more effectively. This is because they will no longer be stuck with one-size-fits-all solutions.
Ultimately, precision medicine is more than simply providing patients with better drugs. It’s about taking a more intelligent and personalized approach to healthcare that will ultimately save lives and improve the overall quality of life for millions of people.