Understanding DNA Profiling and Sequencing Around the World
Have you ever thought about what makes you different and unique from others? The answer lies in your DNA. The genetic material inherited from our parents not only reflects our family legacy. It also holds some of the deepest mysteries of science. Across the world, researchers and clinicians are working to unlock these mysteries. And for that, they are using powerful tools such as DNA Fingerprinting, DNA Sequencing, and advanced DNA analysis.
These technologies have now become integral to medicine, forensic science, agriculture, and evolutionary biology worldwide. If you are curious about this exciting field of science, you are in the right place. Here, we promise to provide you with clear, accurate, and up-to-date information about DNA Fingerprinting.
We will look at some of the most powerful tools that are used. We will explain how gene sequencing and genetic testing are applied across different regions. And at the end of the article, we will understand why these techniques really matter in our modern-day scientific community.
So, let’s dive deeper into this exciting technological breakthrough in science.
What Is DNA Fingerprinting?
Before we understand the basics of life, let’s understand what DNA fingerprinting is. According to the textbooks, it’s a technique used to differentiate individuals based on their DNA.
DNA Fingerprinting, or DNA Profiling, was developed by Sir Alec Jeffreys in the mid-1980s. The method relies on highly variable regions of DNA known as short tandem repeats (STRs) today.
DNA Sequencing and Gene Sequencing Technologies
DNA Sequencing is the process of reading the exact order of the four DNA building blocks (A, T, C, and G) in a DNA sample. Whereas, in Gene sequencing, we look at specific genes. At the same time, whole-genome sequencing examines all of a person’s DNA. These methods help scientists study diseases, identify genetic changes, and improve medical treatments.
Major DNA Sequencing Technologies
| Technology | Description | Global Use |
| Sanger Sequencing | First-generation, highly accurate | Clinical validation, small-scale studies |
| Next-Generation Sequencing (NGS) | High-throughput, cost-effective | Medical genomics, population studies |
| Third-Generation Sequencing | Long-read, real-time sequencing | Structural variation analysis |
With the advancing technology, the next-generation sequencing has dramatically reduced the sequencing cost. This has helped the large-scale projects, such as the Human Genome Project, to be completed successfully. The most interesting fact was that this project was initiated in the UK, China, and the USA.
DNA Analysis and Genetic Testing in Healthcare
With genetic testing, the healthcare sector has changed a lot. This testing has helped us in detecting inherited disorders. It has also guided the scientists in cancer treatment and in predicting disease risk.
Global Applications of Genetic Testing
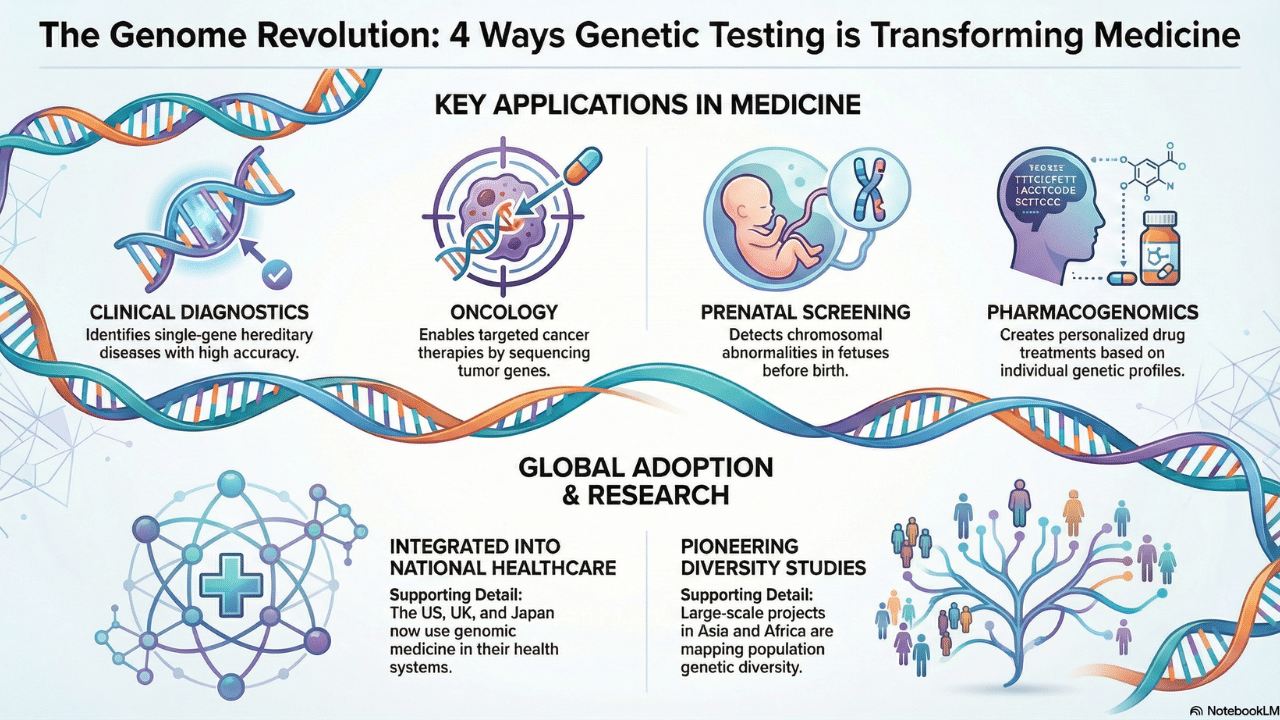
- Clinical diagnostics: Now we can identify monogenic diseases
- Oncology: The researchers can study tumor gene sequencing for targeted therapies
- Prenatal screening: We can detect chromosomal abnormalities in humans and animals
- Pharmacogenomics: With this testing, you can have your personalized drug treatments based on genetic profiles
Today, countries like the US, UK, and Japan use genomic medicine in their national healthcare systems. Whereas, the big projects in Asia and Africa are studying the genetic diversity of their population.
DNA Profiling in Forensics and Law Enforcement
DNA Fingerprinting is widely used in forensic science around the world. Police use DNA to match suspects to crime scenes and to help prove when someone is innocent.
Many countries keep national DNA databases, such as CODIS in the United States and similar systems in Europe and Asia.
Benefits of DNA Fingerprinting and Sequencing
| Benefit Area | Description |
| High Accuracy | DNA Fingerprinting and DNA Sequencing deliver precise identification and reliable genetic analysis |
| Cold Case Resolution | Advanced DNA analysis enables reopening and solving long-standing criminal investigations |
| Medical Advancements | DNA sequencing and genetic testing support early diagnosis, personalized medicine, and targeted therapies |
| Global Research Collaboration | Shared genomic data strengthens international life science research and public health initiatives |
Challenges of DNA Fingerprinting and Sequencing
| Challenge Area | Description |
| Privacy & Data Security | DNA databases raise concerns about unauthorized access and misuse of genetic information |
| Ethical Considerations | Issues include informed consent, data ownership, and familial DNA searching |
| Legal Variability | Differences in national regulations complicate international DNA data sharing |
| Representation Gaps | Limited population diversity in genomic datasets affects research equity and accuracy |
As many countries are working together, it’s important to have standardized protocols and guidelines. INTERPOL sets these common standards for using DNA in forensic investigations.
Ethical, Legal, and Social Considerations
Despite its benefits, DNA profiling and genetic testing raise ethical concerns. These issues include informed consent, data ownership, and potential misuse of genetic information.
Today, we have regulations such as the EU’s General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) and UNESCO’s bioethics guidelines that are used to protect people while supporting scientific advancements. Responsible governance is very important today as DNA sequencing becomes faster and more accessible worldwide.
Key Applications of DNA Fingerprinting
| Application Area | Purpose |
| Forensic science | Criminal identification and evidence matching |
| Paternity testing | Establishing biological relationships |
| Disaster victim identification | Identifying individuals after mass disasters |
| Wildlife conservation | Tracking illegal poaching and biodiversity |
DNA Fingerprinting remains one of the most reliable identification tools. This is due to the extremely low probability that two unrelated individuals share the same DNA profile.
Future Trends in DNA Fingerprinting and Sequencing
The biotech world is moving faster than ever before. The future of DNA Fingerprinting and gene sequencing is now an affordable technology for everyone. The rapid DNA tests are helping identify people in real time, while new DNA sequencing methods and artificial intelligence are making it easier to understand complicated genetic information.
As whole-genome sequencing becomes easier and more affordable, it is expected to play a bigger role in personalized medicine, public health, and scientific research around the world.
Conclusion
Today, when we talk about DNA fingerprinting and DNA sequencing, we know that they are no longer just confined to research labs. They have a real impact on our everyday lives. They help in identifying individuals, solving crime mysteries, and even finding cures for diseases.
With the advancing technology and rapidly evolving scientific world, genetic testing is becoming easier to access. Now the DNA analysis is more accurate than ever before. This has helped our scientists to open new doors in personalized medicine, smarter forensics, and more.
But it’s essential to use these tools responsibly. While the researchers are working across the continents, it’s crucial to safeguard the genetic information. With this, everyone will be able to benefit from DNA technology. When we use these tools carefully, they will teach us more about the fundamentals of life.