Genetic Engineering
Imagine that there is a farmer, living in a drought-prone village. He and his family are scared about the uncertain climate changes. The crops will die if it rains lately. The crops get drowned if it rains heavily. His entire livelihood was a gamble. Now, think of a different timeline. The same farmer plants a modified seed. This seed knows how to hold water content, survive when the sun scorches more, and bear the soil cracks. The farmer can sleep peacefully, not just because the weather changed, but because the crop did. This is the magic of Genetic Engineering.
What is meant by Genetic Engineering?
Genetic engineering is the direct modification or manipulation of the genetic material of an organism. DNA is altered by adding, deleting, or changing genes to introduce or improve specific traits using biotechnological tools. Genetic modifications are performed using Recombinant DNA Technology. Many enzymes are used to cut and paste genes in DNA. In simple terms, life is built on a code called DNA. Consider DNA as a massive instruction manual that tells a cell how to design a bacterium, a vegetable, or even a person.
It is the technology that allows researchers to open that manual, find a specific page, and rewrite a sentence. They may delete a typo that causes a disease, or they may add a paragraph that allows a strawberry to survive in cold conditions.
We also come across Gene Editing. Gene Editing is a precise tool used to modify genes. CRISPR is one of the most widely used gene-editing tools, enabling faster, cheaper, and more accurate DNA editing.
Brief History
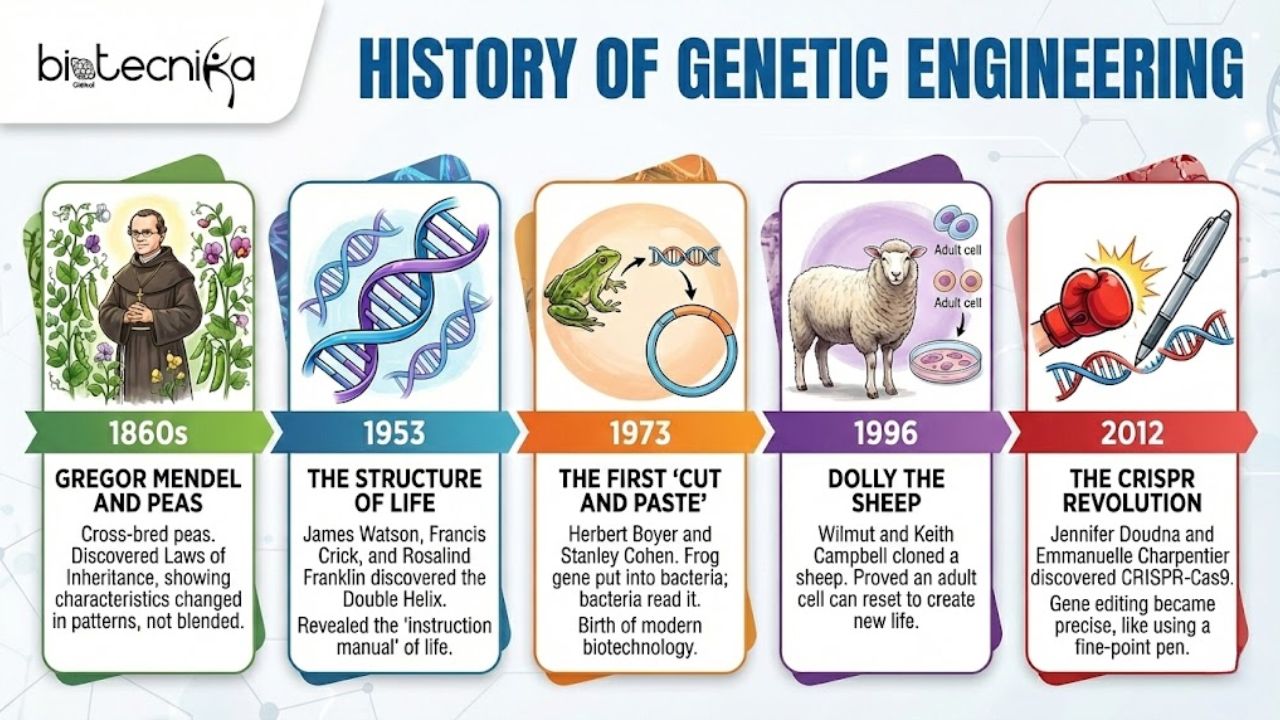
We have to look at the past to understand the future. Genetic engineering did not start with a computer; it all started with a monk in a garden.
- The Monk and the Peas (1860s): Gregor Johann Mendel cross-bred peas. He noticed that characteristics like height or color didn’t just blend like paint; they changed into specific patterns. He discovered the Laws of Inheritance.
- The Structure of Life (1953): James Watson, Francis Crick, and Rosalind Franklin discovered the Double Helix structure of DNA. Finally, we knew what the instruction manual looked like.
- The First “Cut and Paste” (1973): The first successful Genetic Engineering experiment was performed by Herbert Boyer and Stanley Cohen. The gene was taken from a frog and put into bacteria. The bacteria accepted it and began reading the gene of the frog. This was the birth of modern biotechnology.
- Dolly the Sheep (1996): When scientists Wilmut and Keith Campbell cloned a sheep, the world was shocked. This proved that an adult cell can be made to reset to create a new life.
- The CRISPR Revolution (2012): Jennifer Doudna and Emmanuelle Charpentier are the scientists who discovered CRISPR-Cas9. Before this, gene editing was like trying to rewrite a book while wearing boxing gloves. CRISPR took off the gloves and gave us a fine-point pen.
The Original “Cut and Paste”
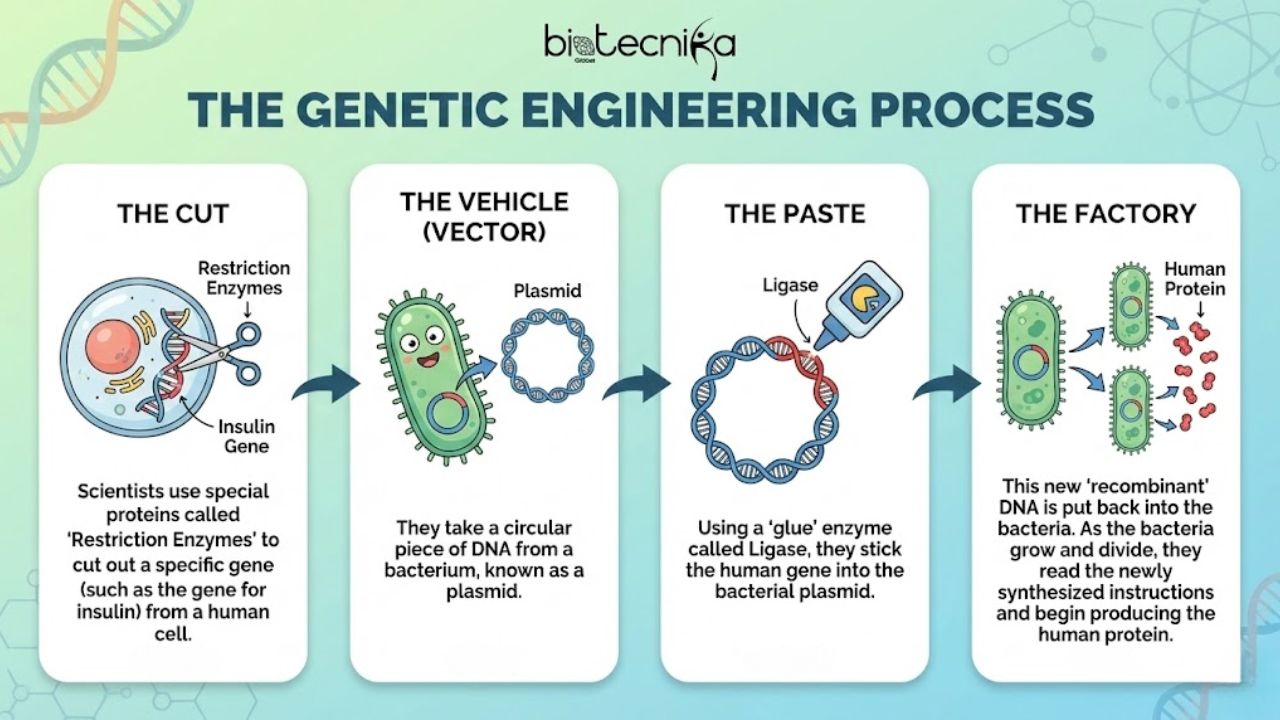
Recombinant DNA Technology is a method for creating a new genetic combination from different sources. Before we had the advanced tools and technologies like CRISPR, this Recombinant DNA Technology was helpful in Genetic engineering. If CRISPR is like a precision laser, rDNA Technology is like using scissors and glue. rDNA Technology is the ancestor of modern genetic engineering. It is still the workhouse of many industries even today.
-
How does it work?
The process is surprisingly similar to making a sandwich:
- The Cut: Scientists use special proteins called “Restriction Enzymes” to cut out a specific gene (such as the gene for insulin) from a human cell.
- The Vehicle (Vector): They take a circular piece of DNA from a bacterium, known as a plasmid.
- The Paste: Using a “glue” enzyme called Ligase, they stick the human gene into the bacterial plasmid.
- The Factory: This new “recombinant” DNA is put back into the bacteria. As the bacteria grow and divide, they read the newly synthesized instructions and begin producing the human protein.
-
Why does this matter?
Before the boom of Genetic engineering, the insulin for treating diabetics was harvested from the pancreases of slaughtered cows and pigs, which often caused allergic reactions. This simple cut-and-paste method is the reason behind the safety of diabetes treatment today. This is because insulin is produced through genetic engineering. Recombinant DNA changed it from a slaughterhouse product to a lab-grown miracle.
Where is Genetic Engineering used?
Genetic engineering not only happens in high-tech research laboratories. Genetics is the study of DNA, Chromosomes, and genes. It can also occur in your fridge or medicine cabinet.
1. Healthcare and Medicine (The Healers)
This is where the most emotional victories happen.
- Gene Therapy: It involves replacing a defective gene with a healthy gene to cure disorders. This seeks to cure Sickle Cell Anemia and blindness.
- Pharma-crops: Researchers are working on edible vaccines. Any fruits and vegetables are modified using vaccine doses.
- Insulin: It is one of the most important discoveries ever made in the field of genetic engineering. Insulin-producing genes were harvested from the pancreas of slaughtered pigs and cows and used to manufacture diabetes medications. Today, researchers use bacteria, such as genetically modified Escherichia coli, to produce pure human insulin. This is safer, cheaper, and more ethical.
2. Agriculture (The Feeders)
We need more food from less land as the global population continues to grow.
- Golden Rice: Rice is engineered to contain Vitamin A. This is designed to prevent blindness in children in developing nations.
- Pest Resistance: Crops like Bt Cotton produce a natural protein that is toxic to specific pests but safe for humans. This is reducing the need for chemical sprays or pesticides.
3. Environment (The Cleaners)
- Bioremediation: This is a fancy word for “nature cleaning up our mess.” Scientists are modifying the bacteria. This could help clean up oil spills at sea or break down plastics in landfills.
Who does this work?
The career opportunities are expanding globally. This is especially for the people who are fascinated by the idea of debugging the code of life. This is not just meant for people with “Doctor” before their names. The industry needs a mixture of talents and young minds.
The Hotspots
- USA (Boston/Cambridge): The Silicon Valley of Biotech.
- United Kingdom: Focuses mainly on genomics and ethics.
- China: Moving incredibly fast in agricultural and medical editing.
- India: A growing hub for agricultural genetics and bioinformatics.
Career Paths in Genetic Engineering
| Job Title | What They Do (Simply Put) | Typical Education Needed | Average Salary Potential (Global/Year) |
| Genetic Counselor | The bridge between science and patients. They explain genetic risks to families. | Master’s in Genetic Counseling | $80,000 – $110,000 |
| Bioinformatician | The data wizard. They use code (Python/R) to analyze massive biological datasets. | Degree in CS + Biology | $90,000 – $130,000 |
| CRISPR Scientist | The editor. They work in wet labs conducting the actual gene editing experiments. | PhD in Molecular Biology | $100,000 – $160,000 |
| Biotech Lawyer | The protector. They handle patents and ethical regulations for new discoveries. | Law Degree + Science background | $150,000+ |
| Lab Technician | The hands. They run the day-to-day machinery and tests. | Bachelor’s in Biotech/Biology | $50,000 – $70,000 |
What is the Next Step?
The future of genetic engineering is the most fascinating pioneer in human history. We are changing our focus from problem-solving to potential enhancement.
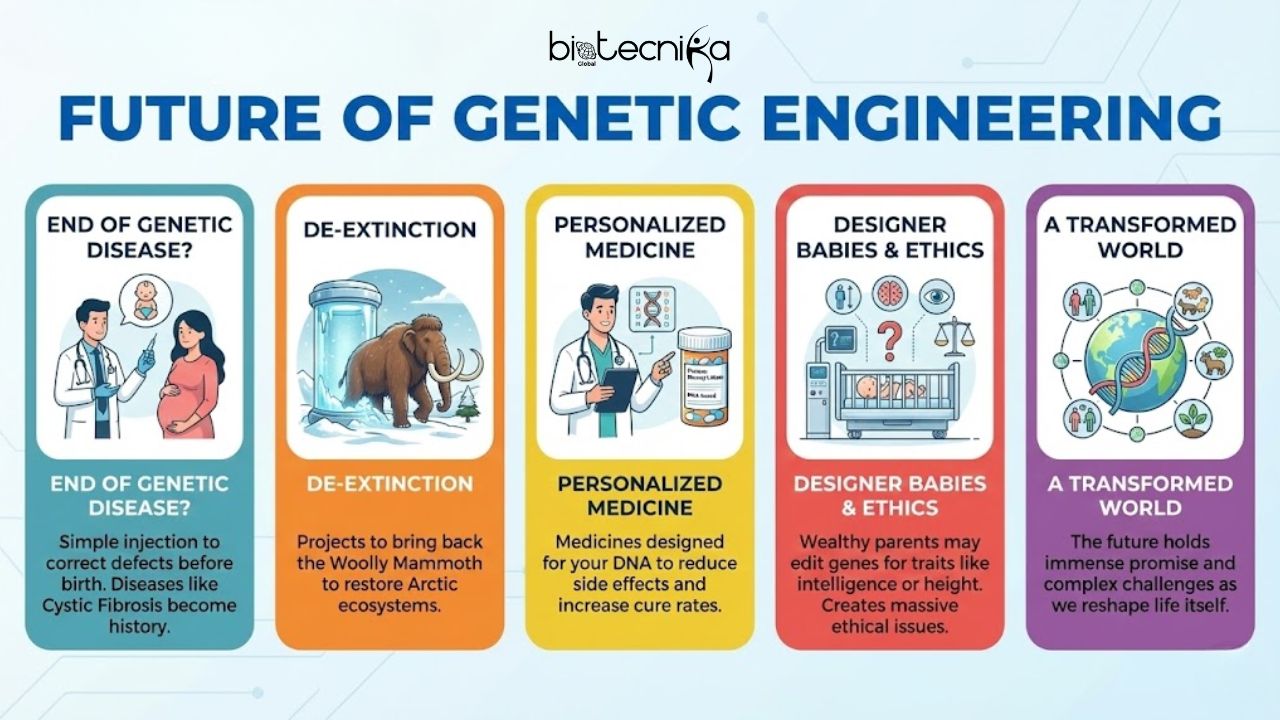
1. The End of Genetic Disease?
The ultimate goal of Genetic engineering is to make sure that diseases like Cystic Fibrosis, Tay-Sachs, and Huntington’s become history books rather than medical realities. It is expected to have a future where a simple injection could correct a heart defect even before a baby is born.
2. De-Extinction
Jurassic Park was fiction, but the science is getting closer. To help restore the Arctic tundra ecosystem, projects are currently ongoing to bring back the Woolly Mammoth.
3. Personalized Medicine
Imagine that you are going to the doctor and you are prescribed personalized medicines instead of getting the same medications that everyone else gets. These personalized drugs could be specifically designed based on your DNA. They gradually reduce side effects and increase the rate of cure.
4. The Ethical Elephant in the Room
We cannot talk about the future without talking about “Designer Babies.” Wealthy parents may edit their children’s genes not just for health but also for height, weight, intelligence, or eye color. But this creates massive ethical issues
Traditional Breeding vs. Modern Gene Editing
| Feature | Traditional Breeding (The Old Way) | Genetic Engineering / Gene Editing (The New Way) |
| Precision | Low. It’s like shuffling a deck of cards and hoping for a good hand. | High. It’s like picking the exact card you want. |
| Speed | Slow. Takes nearly 10-15 years to develop a new crop variety. | Fast. Can be done in 2-5 years. |
| Species Limit | You can only breed a tomato with another tomato. | You can take a gene from a bacterium and put it in a plant. |
| Safety Concerns | Generally accepted as safe for thousands of years. | Rigorously tested, but public fear regarding GMOs remains high. |
Conclusion
We are on the edge of a new era. Genetic Engineering is more than a subject in a biology textbook. It is becoming the technology that will define the 21st century.
Right from the food on our plates to the medicines in our blood, the ability to read and write the code of life is changing everything. This field offers a chance to solve some of the most challenging puzzles for human beings.
Whether you are a coder, a lawyer, a farmer, or a scientist, there is a place for you in this revolution. The book of life is open. Are you ready to help write the next chapter?