Exploring the Power of Multi-Omics in Disease Biology
Scientists today can study diseases at an advanced level thanks to Multi Omics. Multi Omics merges different layers of data about the biology of an organism instead of relying on older methods that use only one type of data to create a full picture of how a disease behaves. The power of using Omics technology allows you to learn about both the genetic code, proteins, and small molecules in the organism. This has revolutionized Disease Biology by increasing speed, accuracy, and personalization in Disease Research.
Multi Omics is not only helping researchers develop new ways of treating diseases; it also provides insight into preventing and predicting future occurrences of these diseases. We will be discussing how Multi Omics functions, its use cases, the difficulties it faces, and the bright future it has within the healthcare industry in this article.
A Quick Look Back: How Disease Research Was Done Before Multi Omics
In the Multi Omics all around the World era, scientists studied different aspects of diseases individually. Doctors, for example, study genetics (Genomics) without considering the influence of other areas such as Proteomics and Metabolomics etc. On their own, each of these methods provided hints to how a patient might be affected by the condition; however, they did not provide a complete representation of their understanding of the patient. Think of trying to understand how a car engine works. If all you studied was the spark plugs of the engine, you would not be able to fully understand the workings of the engine as a whole. Diseases are complex, usually consisting of thousands of components all working together. The advent of Multi Omics has revolutionized how we visualize and study disease biology. By combining numerous omic technologies into one cohesive platform, researchers are able to develop a comprehensive understanding of how diseases originate, evolve, and respond to therapeutic intervention.
What is Multi Omics?
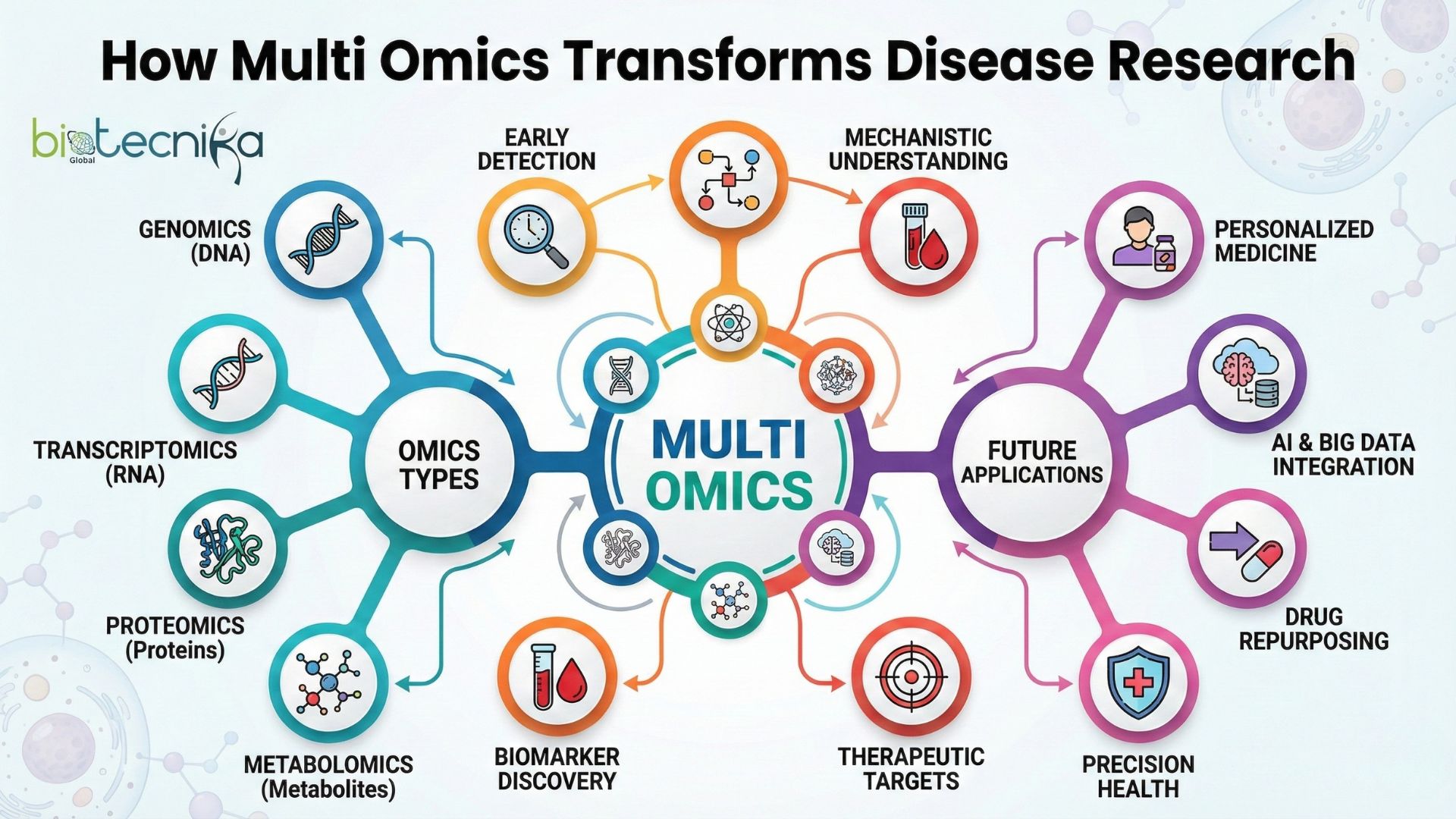
Multi-omics refers to the technique of studying multiple levels of biological information at the same time. The levels studied using Multi Omics are:
- Genomics: This is the study of an organism’s DNA/genetic material as well as genetic variation. Genomics provides information on the relationship between genes and diseases.
- Transcriptomics: This is the study of the RNA molecules that carry the information from the genomes to make proteins. Transcriptomics allows researchers to see what genes are active in certain diseases.
- Proteomics: Proteomics is the study of the proteins in the organism’s cells and how they function, change, or malfunction as a consequence of disease.
- Metabolomics: This is the study of small molecules (sugars, fats, etc.) and their relationship to energy metabolism and disease.
- Integrative Omics: It is the combination of the above four levels of study to create a holistic view of the organism. For example, in breast cancer, the integrative approach enables the researcher to identify the genetic changes associated with breast cancer and study their effects on proteins as well as identify changes in cellular metabolism.
The utilitization of Multi Omics enables researchers to ascertain the influence of alterations made to DNA upon numerous subsequent layers (including protein expression, changes to metabolic pathways and ultimately leading towards developing into a disease), all of which are essential to comprehend the underlying mechanisms of many complex diseases including cancer and diabetes as well as their effect on an individual’s overall health status.
How Multi Omics Helps in Disease Research
Disease Biology in Detail
Multi Omics has provided researchers with a deeper understanding of Disease Biology than what was possible using traditional techniques. In leukaemia, for example, Multi Omics has allowed researchers to discover new abnormal proteins and identify metabolic pathways that have been altered due to the cancer. This knowledge allows for the development of specific treatments designed to target the abnormalities identified through Multi Omics analyses.
Detecting Disease Early
The earlier a person receives a diagnosis of a disease, the better the chance of successful treatment. The application of Omics technologies allows healthcare providers to identify indicators of potential disease. In other words, biomarkers can be detected much earlier than they would be able to using non-Omics methods. As an illustration, when examining patients with heart disease, researchers are able to detect very small changes in their proteins and/or metabolites years prior to a patient suffering a heart attack. Similarly, Multi Omics has made it possible for researchers to identify genetic mutations and/or protein changes associated with early tumour formation. Detecting diseases in their earliest stages leads to better outcomes for those diagnosed and leads to improved survival rates.
Personalized Medicine
Every person has a unique response to medicine. Multi Omics gives physicians the ability to create custom-made therapies based on the total RNA, DNA, proteins and metabolites of a patient. Therefore, by evaluating all of an individual’s omics, physicians can make better decisions about which treatments will work best for that person.
For example, if two patients have the same breast cancer diagnosis, they might receive completely different medications, depending on each patient’s omics profile. This custom-made approach reduces potential side effects and improves the likelihood of successful treatment.
Identifying Potential New Drug Targets
Historically, most of drug discovery has been conducted using the trial and error method. Multi Omics enables researchers to identify the exact pathways and molecules needed to develop drugs more quickly.
For example, proteomics data from COVID-19 patients allowed scientists to identify various proteins associated with the condition. This information helped researchers create antiviral medications. Multi Omics gives researchers direction, focusing on the critical biological factors for developing effective and safe medications.
Multi Omics and Global Health
The benefits of Multi Omics extend beyond just the treatment of individual patients. Researchers now utilize Multi Omics to monitor disease outbreaks, assess how lifestyle factors influence population health and examine the interaction of non-communicable and communicable diseases.
For example, Metabolomics studies have revealed how urban pollution and diet together contribute to metabolic syndrome in large populations. By combining this with genomics and proteomics, public health policies can be better designed to prevent disease.
Examples of Omics Technologies in Action
Here’s how different omics technologies are applied in disease research:
- Genomics: Identifying mutations in BRCA genes that increase breast cancer risk. Also used to study genetic predispositions to heart disease and rare genetic disorders.
- Transcriptomics: Understanding which genes are switched on in diabetic patients. Helps identify pathways involved in inflammation and autoimmune diseases.
- Proteomics: Studying protein changes in COVID-19 patients and autoimmune disorders like rheumatoid arthritis. Helps find biomarkers and therapeutic targets.
- Metabolomics: Tracking metabolites in diabetes and metabolic syndrome to monitor disease progression. Also used in studying obesity and lifestyle-related conditions.
- Integrative Omics: Alzheimer’s research combines genomics, proteomics, and metabolomics to understand disease mechanisms and discover potential interventions.
Examples of Multi Omics and Their Use in Disease Biology
| Omics Type | What It Studies | Example in Disease Research | Impact on Disease Biology |
| Genomics | DNA, genetic mutations | Identifying cancer-causing gene mutations | Helps detect diseases early and predict risk |
| Transcriptomics | RNA, gene expression | Understanding which genes are active in diabetes | Reveals how genes contribute to disease |
| Proteomics | Proteins and their functions | Studying protein changes in viral infections and autoimmune disorders | Helps find new drug targets |
| Metabolomics | Small molecules & metabolism | Tracking metabolic disorders like diabetes and obesity | Shows how metabolism affects disease |
| Integrative Omics | Combining all omics layers | Alzheimer’s research combining genes, proteins, and metabolites | Gives a complete picture of disease biology |
Challenges in Multi-omics Research
Even though Multi Omics is powerful, it comes with some challenges:
- Large Data: Multi Omics generates huge amounts of data. Managing and analyzing it requires powerful computers and software. AI and big data tools are helping scientists handle this complexity.
- Complex Analysis: Integrating genomics, proteomics, and metabolomics data is complicated. Researchers need specialized training and advanced tools.
- Cost: Multi-omics research can be expensive. However, collaborative studies and open-access data are making it more accessible worldwide.
- Ethical Concerns: Handling genetic data requires privacy and security measures to protect patients.
Despite these challenges, Multi Omics remains one of the most promising approaches in modern Disease Biology research.
Future of Multi Omics
The future of Multi Omics looks extremely bright. Here’s what to expect:
- Predictive Diagnostics: AI models using Multi Omics data will predict diseases before they appear.
- Personalized Therapies: Treatments will be fully tailored to an individual’s unique omics profile.
- Rare Disease Research: Multi Omics will help understand diseases that were previously mysterious due to their complexity.
- Integration with Technology: Wearable devices may continuously monitor metabolites and proteins, giving real-time disease risk data.
- Global Collaborations: Multi-omics data sharing across countries will accelerate research and discovery.
- Drug Development: New drug targets will be discovered faster, making treatments safer and more effective.
The combination of omics technologies, AI, and big data will revolutionize Disease Biology in the next decade.
Top 5 Impacts
- Better Understanding of Disease Mechanisms: Scientists can see how genes, proteins, and metabolism interact.
- Early Detection: Biomarkers identified through Multi Omics allow doctors to detect diseases before symptoms appear.
- Personalized Medicine: Treatments tailored to a patient’s unique biological profile improve outcomes.
- Faster Drug Discovery: Critical molecules and pathways can be targeted efficiently.
- Public Health Advancements: Population-level Multi Omics studies help design better preventive measures.
Conclusion
In simple words, Multi Omics is transforming the way we study and treat diseases. By combining different omics technologies, scientists get a complete view of how diseases start, progress, and respond to treatment.
From early diagnosis to personalized therapies and new drug development, Multi Omics is changing medicine for the better. Its impact on Disease Biology is huge and will continue to grow, making healthcare more precise, efficient, and effective.
If you’re curious about the future of medicine, Multi Omics is definitely the path to watch.