Australian Biotech Firm Vaxxas Set For Clinical Trials Of Skin-Patch Delivered Covid Vaccine
From the outset of the Covid-19 outbreak, scientists were determined to make transdermal drug delivery patches, a breakthrough that could transform medicine.
This life-saving technique could be quite useful for individuals with a phobia of syringes and children scared to go to a doctor.
Apart from that, skin patches could heighten the efficiency of vaccines and facilitate easy distribution as they do not have any cold-chain needs.
Promising results were shown in recent research with rodents. The findings are published in Science Advances.
The US-Australian research team employed 1 sq cm patches dotted with over 5000 microscopic spikes, which are not visible to the naked eye, according to the statement given by the co-author of the study and the University of Queensland‘s virologist, David Muller to AFP.
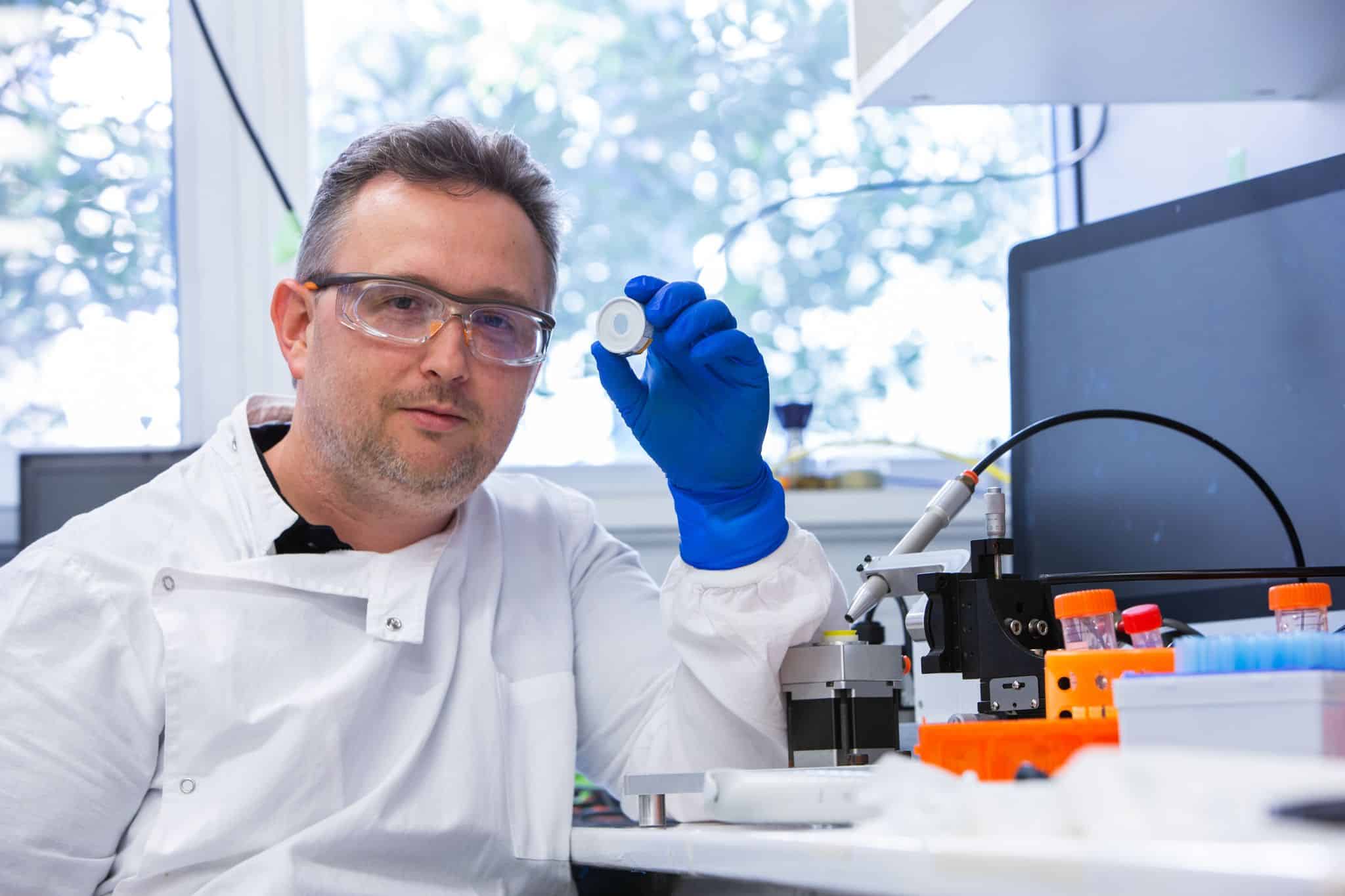

Muller added that these spikes have experimental vaccine coatings and the patch is turned on using an applicator that looks like a hockey puck. It feels like getting a good flick on the skin.
The scientists employed a subunit vaccine that replicates the spikes present on coronavirus’s surface.
Rodents were subjected to two methods- using syringe & patch over the course of 2 minutes- to compare the effects of both.
The immune systems of rodents who received the vaccine via the patch demonstrated high neutralizing antibody levels followed by 2 doses, even in their lungs, which is crucial to prevent Covid-19. The study indicated that patches outdid the syringes.
They also discovered that another sub-group of rodents, who received just a single vaccine dose with an adjuvant (an extra element added to trigger the immune reaction), did not get sick at all
Convenient To Use
What makes these skin patches so special?
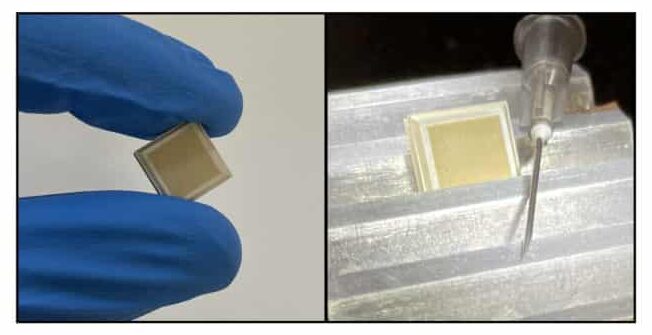
Muller explained that vaccines are generally administered into muscles, however, tissue present in muscle does not have that many immune cells to respond to the drug.
Besides that, the microscopic spikes induce localized skin death, which eventually alerts the body about the issue and activates the immune system.
For the researchers, the logistical benefits could not be clearer.
When compared to a couple of hours at room temperature for Pfizer & Moderna vaccines, the initial dry coating of the vaccine on the patch showed stability for at least 1 week at 40°C (104°F) and 1 month at 25°C (77°F).
This gives a significant edge specifically for developing nations.
Muller said that the next feature of the needle-free vaccine patch is that it is very easy to use. There is no need for any well-trained healthcare professional to use it.
Additionally, Burak Ozdoganlar, an engineering professor from Carnegie Mellon University, Pittsburgh, the US, has been working on developing this technology since 2007.
He elucidated another benefit while discussing with AFP that a specific and right quantity of vaccine dermally administered triggers an immune response like intramuscular delivery. It is a crucial aspect since the world is struggling with Covid-19 vaccine procurement.
Ozdoganlar can manufacture about 300 to 400 patches daily in his laboratory, however, has not tried with mRNA vaccines, which emerged during the outbreak, since Moderna or Pfizer has not authorized his work.
The Future
The needle-free vaccine patch employed for the research mentioned in the publication was created by an Australian firm called Vaxxas. Studies on humans are expected to be performed by the month of April.
2 other US firms are also competing in the race: Vaxxas & Micron Biomedical.
Massachusetts-based Vaxxas, established in 2013, is currently focusing on a slightly distinct kind of patch having dissolving microneedles when subjected dermally.

They mentioned that this method has the advantage of needing much fewer spikes for each patch (121), which consists of a biocompatible protein polymer.
Michael Schrader, the CEO while talking to AFP explained that they are focusing on seasonal flu and Covid combination product that will be delivered directly to the house of the patients for them to administer on their own.
The Covid-19 vaccine employed here is manufactured by the firm Medigen, which is already approved in Taiwan.
Australian biotech firm, Vaxxas has recently started a manufacturing unit near Boston, with a grant from NIH, the US. They intend to manufacture sufficient skin-patch delivered Covid vaccine for 2000-3000 individuals in clinical studies which are to be distributed by the upcoming summer.
The major hurdle faced right now is manufacturing as no company is yet capable of making sufficient patches on large scale.
Schrader claimed that if one intends to launch a vaccine then they have to manufacture hundreds of millions, which is currently not available.
He also told that the Covid-19 pandemic, on the other hand, has driven the nascent industry, which is currently attracting many investors.
Schrader asserted that this is the future and is inevitable according to his opinion. He believes that this technology is going to revolutionize the way in which vaccines are delivered throughout the world.
Skin-Patch Delivered Covid Vaccine, Australian Biotech Firm Vaxxas, Needle-Free Vaccine Patches, Vaxxas’ Needle-Free Vaccine
Also Read:
- Can A Quick Breathalyzer Test For COVID-19 Replace Nasal Swab Test?
- Cleveland Clinic To Begin Clinical Trials For The First-of-Its-Kind Breast Cancer Vaccine
- The Pupil Can Assess Numerical Information Apart From Light
- MIT Scientists Discover New Cancer Therapy To Awaken The Immune System
- A New Study Shows That Plants Talk To Neighbors Using RNA



